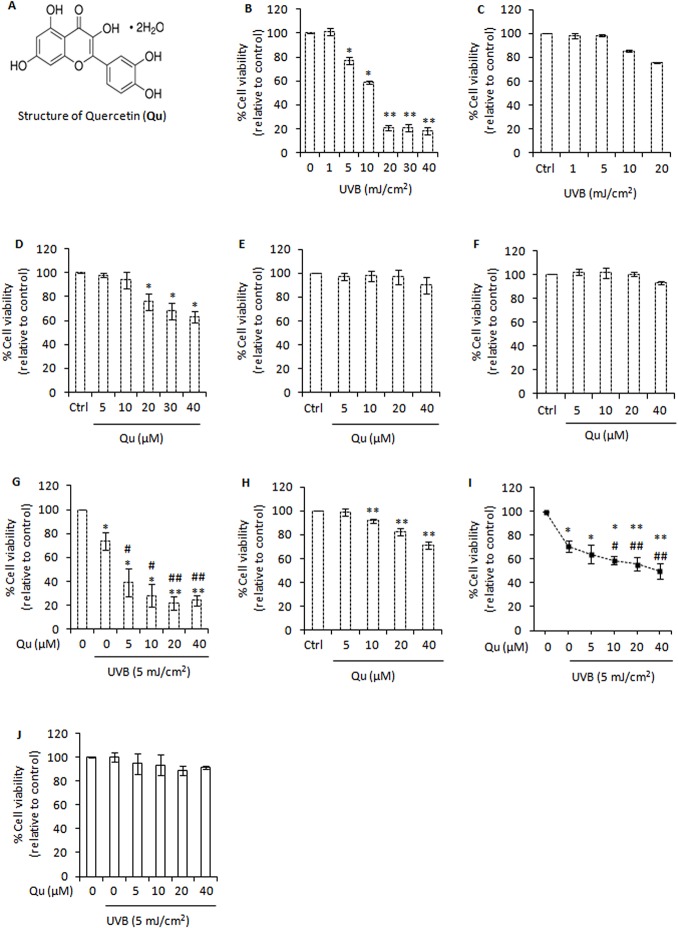
Fig 1. Quercetin promotes UVB-induced cell death.
A, structure of quercetin (Qu). B, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in B16F10 cells at 24 h post-UVB irradiation. Columns, mean of three experiments; bars, SD. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01 for control versus treated. C, analysis of cell viability in Hs68 human fibroblast cells at 24 h post-UVB irradiation. D, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in B16F10 cells treated with Qu. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01 for control versus Qu treated. E, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in human HaCaT keratinocytes at 24 h post-Qu treatment. F, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in Hs68 human fibroblast cells at 24 h post-Qu treatment. G, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in B16F10 cells treated with Qu and/or UVB (5 mJ/cm2) for 24 hours. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01 for control versus treated; #, P<0.05; ##, P<0.01 for UVB-alone treatment versus UVB + Qu treatments. H, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in A375 human melanoma cells at 24 h post-Qu treatment. I, analysis of cell viability using the MTT assay in A375 cells treated with Qu and/or UVB (5 mJ/cm2) for 24 hours. J, analysis of cell viability in Hs68 cells treated with Qu and/or UVB for 24 hours.