Figure 1.
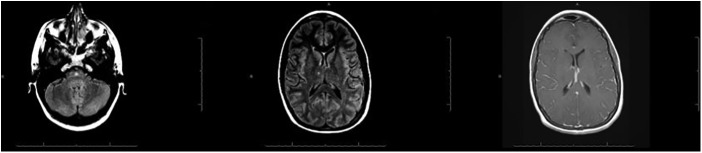
MRI of the brain at admission showing diffuse abnormal hyperintensities within the sulci of both cerebral hemispheres associated with abnormal leptomeningeal enhancement; these findings were consistent with meningitis. The MRI also showing two small, non-specific foci of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery hyperintense signals in the R thalamus and lower pons.
