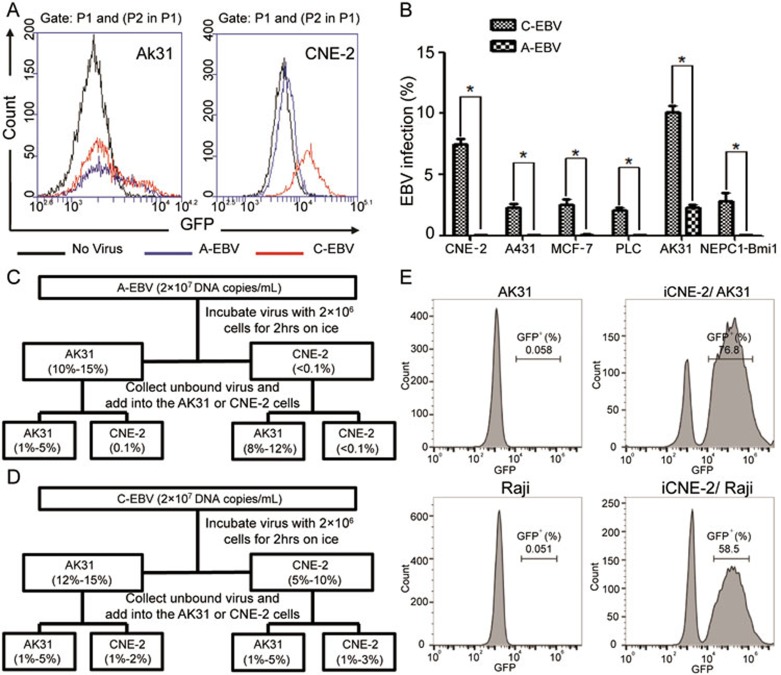
Figure 3.
EBV from in-cell infected CNE-2 cells possesses enhanced infection potency and altered tropism. (A) Determination of GFP+ AK31 cells (left) and CNE-2 cells (right) after the infection with A-EBV from GFP-Akata cells (blue line) or C-EBV from iCNE-2 cells (red line) for 24 h by flow cytometry. Cells without EBV treatment served as negative control (black line). (B) Statistical comparison of percentages of CNE-2, A431, MCF-7, PLC/PRF/5, AK31 and NEPC1-Bmi1 cells with GFP expression after 24 h cell-free infection with A-EBV or C-EBV by immunofluorescence microscopy. All experiments were repeated at least three times. *P < 0.05. (C, D) Absorption assay of A-EBV (C) or C-EBV (D) was performed. 2 × 107 DNA copies/ml A-EBV (C) or C-EBV (D) virus was incubated with 2 × 106 AK31 or CNE-2 cells for 2 h on ice. Supernatants were collected and the fresh medium was added to cells for culture. The percentage of GFP+ AK31 or CNE-2 cells was determined by flow cytometry after 12 h. The collected supernatants were added to fresh AK31 and CNE-2 cells to determine the infection rate after 12 h. (E) AK31 or Raji cells were co-cultured with in-cell infected iCNE-2 cells for 24 h. The expression of GFP in AK31 (upper) or Raji (lower) cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. AK31 and Raji cells only (left) served as negative controls.