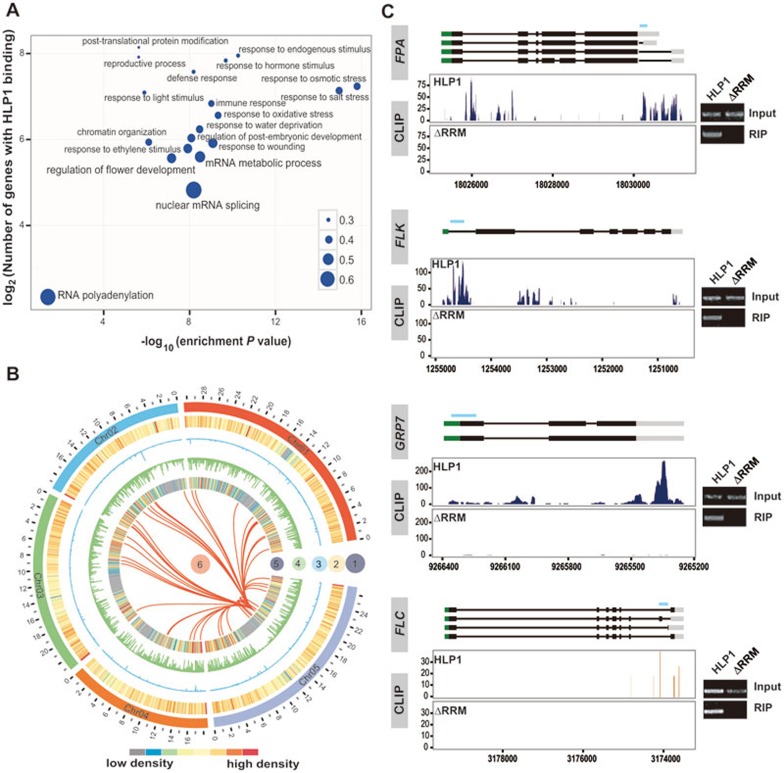
Figure 3.
Enriched HLP1 binding to floral genes. (A) Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of HLP1 binding targets. Significantly enriched GO terms of genes with HLP1 binding were identified using the BiNGO software (hypergeometric test with Benjamini and Hochberg false discovery rate correction). The x axis indicates the enrichment P-value on a −log10 scale; the y axis indicates number of genes with HLP1 binding on a log2 scale. The size of each point is proportional to the ratio of HLP1-bound genes associated with one GO term to all genes associated with this GO term. (B) Circos diagram shows enriched HLP1 binding sites at flowering-related transcripts: circle 1, Arabidopsis chromosomes (indicated as chr01-05 with different colors); circle 2, heat map displaying all of Arabidopsis genes; circle 3, binding density of HLP1ΔRRM showing very few binding peaks of the truncated HLP1; circle 4, binding density of HLP1 indicating all the HLP1 binding sites across the transcriptome; circle 5, heat map view of genes with HLP1 binding; circle 6, red link lines indicating flowering-related transcripts with HLP1 binding. (C) Examples and validations of flowering associated genes bound by HLP1. Binding sites are shown as wiggle plots on the left. CDS regions are boxed in black and the 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR are boxed in green and grey, respectively. Introns are indicated as lines. Blue line above gene structure indicates RIP-RT-PCR amplified region. The x axis indicates genome site in chromosome. The y axis indicates normalized HITS-CLIP/CLIP-seq abundance. HITS-CLIP/CLIP-seq tag counts were normalized to tag per 10 million (TP10M) to adjust for differences of two HITS-CLIP/CLIP-seq libraries in sequencing depth. Blue for binding peaks at FPA, FLK, GRP7 sense transcripts and orange for peaks at FLC antisense transcripts. Right panels show validation of binding by RIP-RT-PCR.