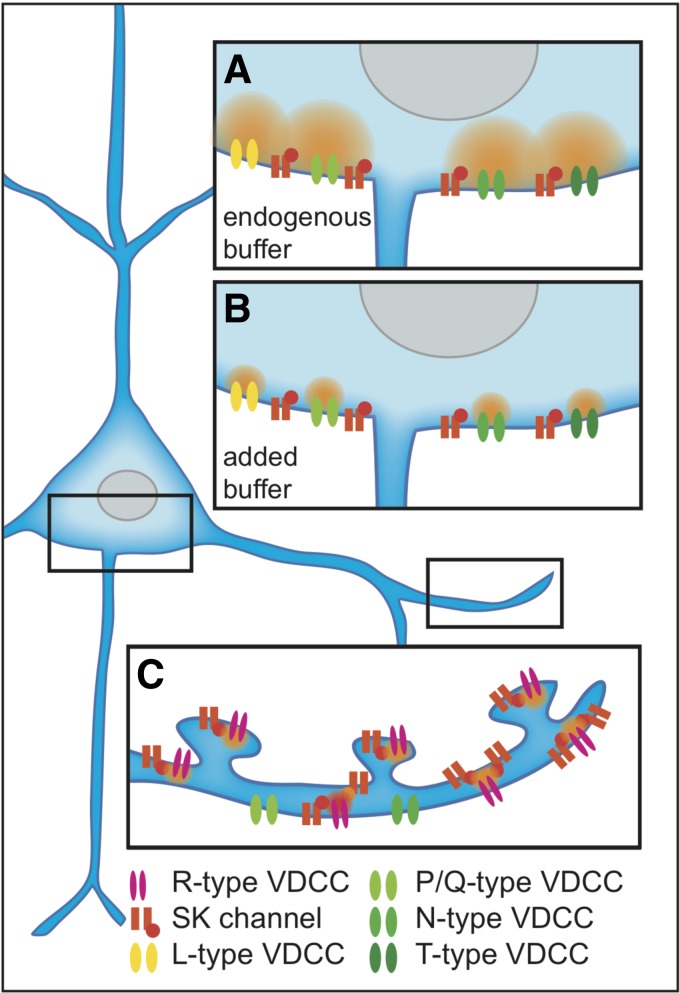
Fig. 1.
Schematic shows a layer V pyramidal neuron. Black boxes indicate somatic and dendritic compartments. A: enlarged somatic compartment containing multiple types of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) that provide calcium (orange cloud) to small-conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channels in microdomain vicinity when endogenous buffer capacity is low. B: same somatic compartment but in the presence of exogenous buffer. The high-affinity buffer constrains the calcium domains, preventing SK channel activation. C: enlarged basal dendrite compartment containing R-type calcium channels in nanodomain proximity to SK channels. Because of the nanodomain relationship of R-type calcium channels and SK channels, exogenous buffer does not interfere with SK channel activation.