Fig. 1.
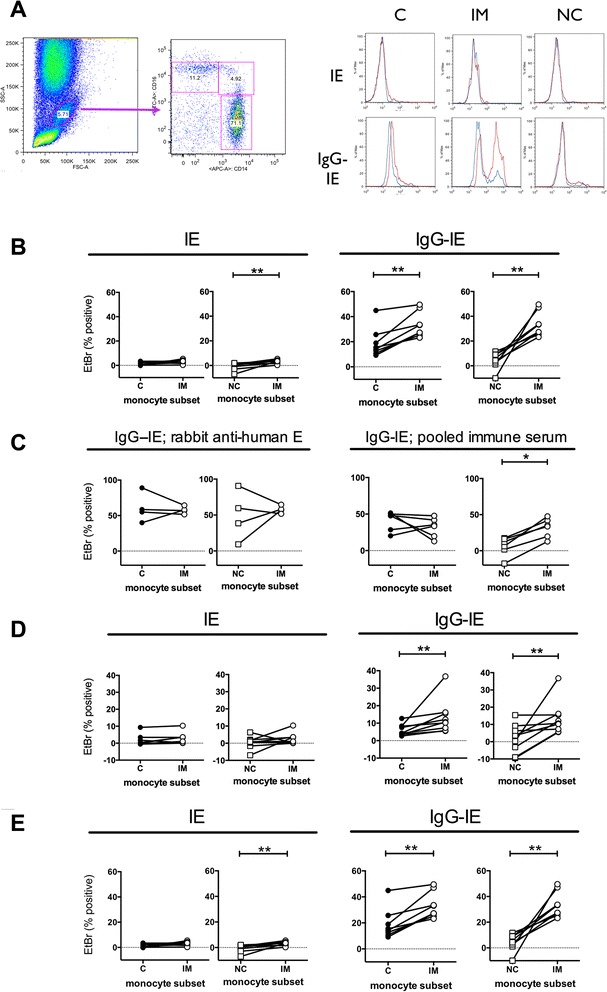
CD14hiCD16+ intermediate monocytes phagocytose IE more efficiently than other monocytes. a Whole blood was incubated with EtBr-labelled CS2-IE for 30 minutes then uningested RBC removed by hypotonic lysis and washing. Cells were stained with anti-CD14 and CD16, monocytes gated using forward and side scatter then subsets defined as classical (C: CD14hiCD16-), intermediate (IM: CD14hiCD16+) and non-classical (NC: CD14loCD16+) as shown. Histograms show EtBr staining of the three subsets incubated at 37 °C (red histograms) or 4 °C (blue histograms) with unopsonised (IE, top) or opsonised (IgG-IE, bottom) IE. b Phagocytosis using blood from eight separate donors. Whole blood was incubated as in a with unopsonised CS2-IE (left hand panels; IE) or CS2-IE opsonised with rabbit anti-human RBC antibody (right hand panels; IgG-IE) as indicated. c Phagocytosis by monocyte subsets of IE opsonised with rabbit anti human RBC was measured using PBMC prepared from four separate donors (left hand panels). Phagocytosis of IE opsonised with pooled human immune serum was measured using PBMC prepared from six separate donors (right hand panels). d Phagocytosis of unopsonised CS2-IE (left hand panels; IE) and CS2-IE opsonised with pooled human immune serum (right hand panels; IgG-IE) was measured in a whole blood assay as in a using blood from nine separate donors. e Phagocytosis using blood from six separate donors. Whole blood was incubated as in a with unopsonised E8B-IE (left hand panels; IE) or E8B-IE opsonised with rabbit anti-human RBC antibody (right hand panels; IgG-IE) as indicated. Background phagocytosis measured at 4 °C was subtracted from all data points. The percent phagocytosis by intermediate (IM) monocytes was compared using pairwise comparisons in each case (b-e) with either that by classical (C) monocytes or non-classical (NC) monocytes, as indicated. Differences between groups were assessed using Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank test: * p < .05, ** p <0.01. EtBr ethidium bromide, IE infected erythrocytes, PBMC peripheral blood monocytes; RBC red blood cells
