Fig. 2.
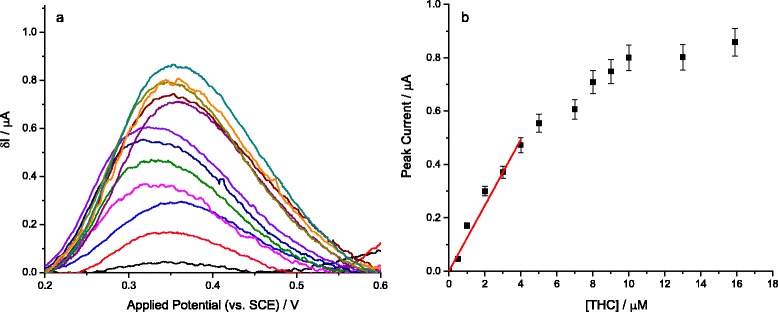
a Square wave voltammograms (frequency: 100 Hz, amplitude: 40 mV, step potential: 1 mV) for the oxidation of THC, seen at ca. +0.35 V (vs. SCE), on the graphite/mineral oil paste electrode. The measurement was obtained in a deoxygenated BBS (0.1 M KCl, pH = 10.0, 298 K), after immersing the electrode in identical stationary solutions that contained 0.50 – 16 μM THC, for 5 min. b The increase of the peak current with increasing THC concentration (black squares) with the correlation line through the linear range (red line, R2 = 0.95). The lower practical limit of detection was determined as being 0.50 μM, while the slope of the calibration curve gave a value of 0.12 μA μM−1 for the sensitivity of the sensor. The errors relate to separate electrode preparations
