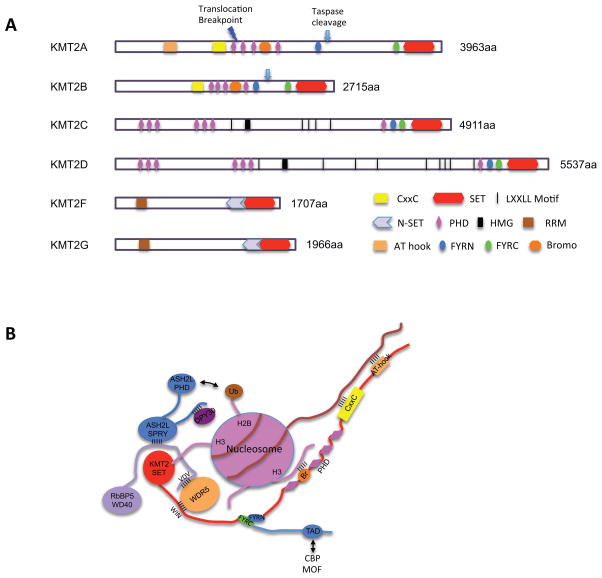
Figure 1. Metazoan KMT2 family histone methyltransferases.
a. Schematic representation of domain structures for each KMT2. KMT2A and KMT2B have the consensus D/GVDD sites (indicated by arrow) that are cleaved by Taspase 1, at two conserved sites for KMT2A and at one conserved site for KMT2B. This cleavage unique feature for this KMT2 subgroup. The resulting large N-terminal fragment and a smaller C-terminal fragment subsequently associate through FYRN and FYRC domains to generate a functional, noncovalent heterodimeric complex. KMT2C and KMT2D contain two clusters of PHD domains as well as the juxtaposed FYRN, FYRC and the SET domains on the C-terminus. One HMG-I binding motif and multiple nuclear receptor interacting motifs (LXXLL) are present in the protein sequences. These motifs are frequently found in transcription factors and cofactors. The PHD4–6 domains of KMT2C and KMT2D are able to bind unmethylated and asymmetrically di-methylated H4 arginine 3 (H4R3me0 and H4R3me2a), supporting a coordinated function with protein arginine methyltransferases.49 KMT2F and KMT2G are the smallest KMT2 subgroup and contain an N-terminal RNA recognition motif (RRM) and a C-terminal N-SET domain, which interact with WDR82 and ubiquitylated histone H2B respectively.
b. Schematic representation of interactions among KMT2A core subunits as well as their interactions with chromatin. KMT2A core complex is stabilized by pair-wise interactions between KMT2A (WIN)-WDR5, WDR5-RbBP5 (VDV), RbBP5-ASH2L and ASH2L-DPY30. KMT2A, pink; WDR5, blue; RbBP5, green; ASH2L, purple; DPY30, red. Furthermore, KMT2A is stabilized on chromatin through multivalent interactions, which include interactions of the AT hook and CxxC domain with AT-rich sequence 189 and non-methylated CpG dinucleotides 70, respectively; as we as interactions between PHD and Bromo-domains with H3K4me3 and acetylated lysine residues, respectively.72 The coupling of the enzyme with binding domains for its methylation product(s) is important for feed-forward maintenance of H3K4me in cells. Transient interactions between SET and histone H3 tail as well as ASH2L PHD and ubiquitin are also reported.