Fig. 1.
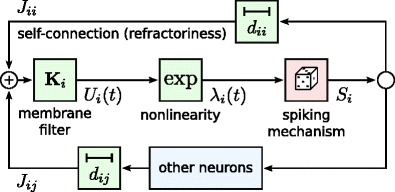
Schematic of the point process generalized linear model (PP GLM) of a recurrent spiking neuronal network. In this model, the spike trains from the neurons in the network, after incurring transmission delays d ij, pass through a linear filtering stage K i. The resulting (pseudo) membrane potential U i(t) is fed into a nonlinear link function , which transforms it into the conditional intensity function λ i(t). The latter drives the probabilistic spiking mechanism that generates an output spike train S i for the i-th neuron. Note that this spike train is then also fed back as an input to the neuron itself via a “self-connection” in order to model its refractory, post-spike properties
