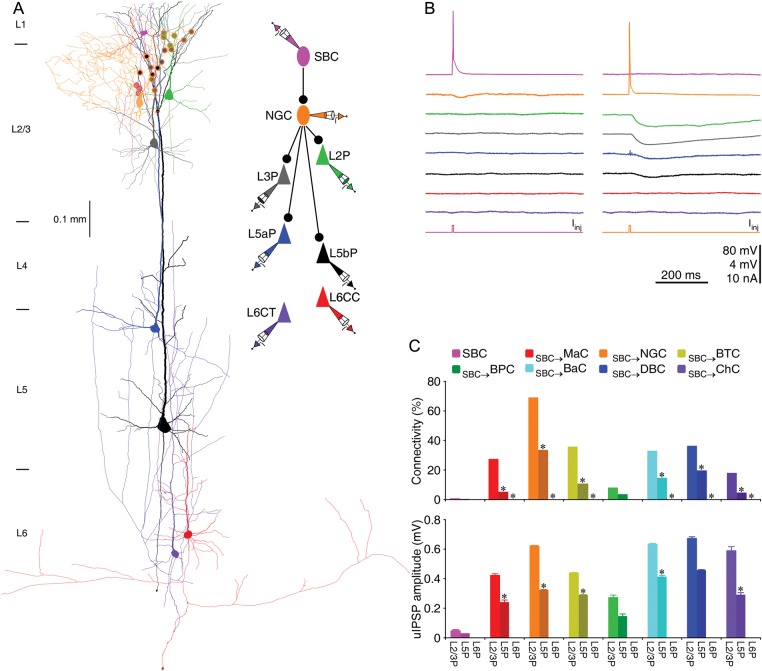
Figure 1.
SBC → L2/3 interneuronal circuits disinhibit L2/3 and L5, but not L6 pyramidal neurons. (A) Reconstruction of L1 SBC (pink), L2 NGC (brown), and 2 L2/3 (L2P and L3P; green and gray), 2 L5 (L5aP and L5bP; blue and black), 2 L6 (CC or L6CC and CT or L6CT; red and purple) pyramidal neurons recorded simultaneously from an acute cortical slice. The double colored dots indicate the putative synaptic contacts based on anatomical reconstruction. The schematic drawing shows symbolically the synaptic connections. (B) Single action potentials elicited in SBC and NGC evoked uIPSPs in postsynaptic NGC, L2/3 and L5 pyramidal neurons, respectively. Scale bars apply to all recording traces with 80 and 4 mV bars applied to traces with and without action potentials, respectively. (C) Connectivity and strength of synapses formed by SBC → L2/3 interneuronal circuits on L2–6 pyramidal neurons. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) in synaptic connectivity (χ2-tests) or synaptic strength (Mann–Whitney rank-sum tests) between SBC → L2/3 interneuronal circuits on L2/3 pyramidal neurons and L5 or L6 pyramidal neurons (see Tables 3–6 for values).