Abstract
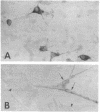
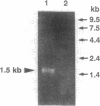
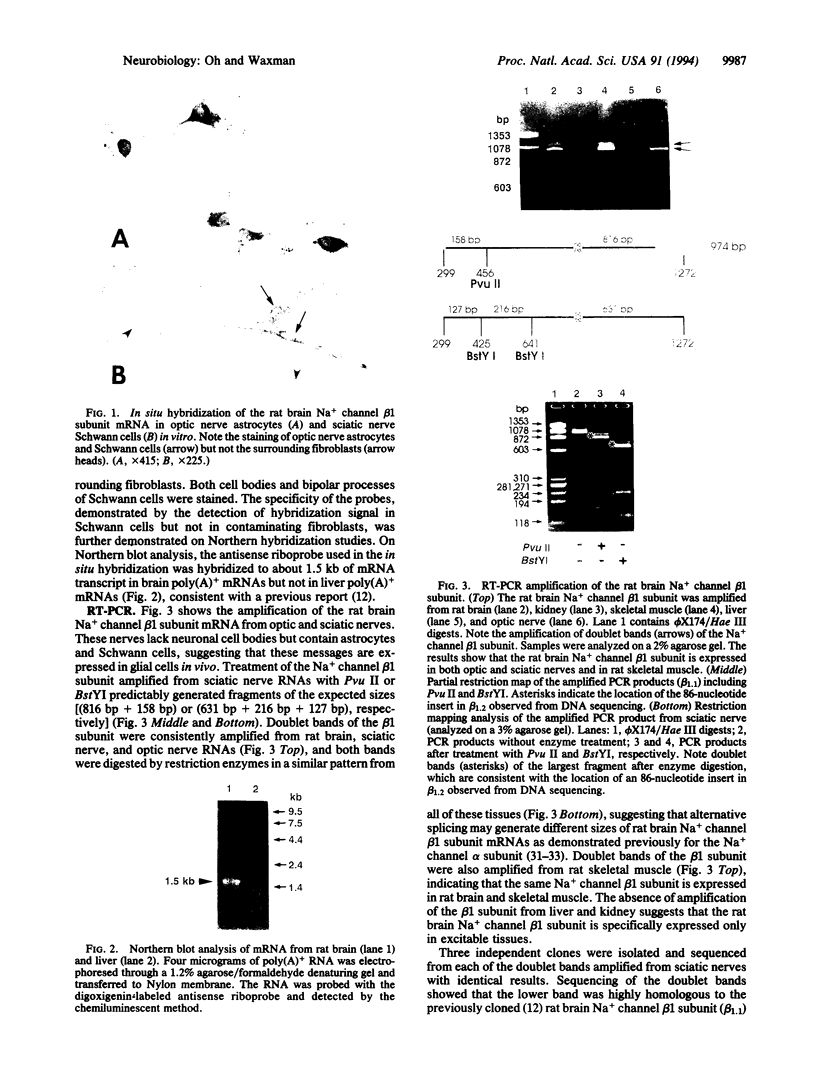
Although the molecular characteristics of glial Na+ channels are not well understood, recent studies have shown the presence of mRNA for rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunits in astrocytes and Schwann cells. In this study, we asked whether the mRNA for the rat brain Na+ channel beta 1 subunit is expressed in glial cells. We performed in situ hybridization using a complementary RNA probe for the coding regions of the rat brain Na+ channel beta 1 subunit mRNA and detected beta 1 subunit mRNA in cultured rat optic nerve astrocytes and sciatic nerve Schwann cells. The beta 1 subunit was amplified by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in rat optic and sciatic nerves, which lack neuronal somata but contain astrocytes and Schwann cells, respectively. Doublet bands of the beta 1 subunit mRNA were amplified from both optic and sciatic nerves. Through the cloning and sequencing of these bands, we confirmed the amplification of a mRNA highly homologous to the previously cloned rat brain Na+ channel beta 1 subunit (beta 1.1) and a novel form of the beta 1 subunit mRNA (beta 1.2), which is closely homologous to beta 1.1 but contains an additional 86-nucleotide insert in 3' noncoding regions. Two beta 1 subunit mRNAs were also amplified from rat brain and skeletal muscle, but not from rat liver or kidney. These results indicate that rat brain Na+ channel beta 1 subunit mRNAs are expressed in glial cells as well as in neurons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Moore A. C., Levinson S. R., Raftery M. A. Identification of a large molecular weight peptide associated with a tetrodotoxin binding protein from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):860–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90782-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):449–461. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Probing the molecular structure of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:455–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Protein components of the purified sodium channel from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1377–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Chun L. L., Corey D. P. Glial and neuronal forms of the voltage-dependent sodium channel: characteristics and cell-type distribution. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1375–1388. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Chun L. L., Corey D. P. Ion channel expression by white matter glia: I. Type 2 astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Glia. 1988;1(1):10–30. doi: 10.1002/glia.440010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Koroshetz W. J., Chun L. L., Corey D. P. Ion channel expression by white matter glia: the type-1 astrocyte. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90091-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckh S. Differential expression of sodium channel mRNAs in rat peripheral nervous system and innervated tissues. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Chiu S. Y., Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. The presence of voltage-gated sodium, potassium and chloride channels in rat cultured astrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):299–313. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. A., Yokoyama S., Waxman S. G., Oh Y., Zur K. B., Sontheimer H., Higashida H., Ransom B. R. Sodium channel mRNAs in cultured spinal cord astrocytes: in situ hybridization in identified cell types. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 May;23(3):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., McClatchey A. I., Gusella J. F. Modification of the Na+ current conducted by the rat skeletal muscle alpha subunit by coexpression with a human brain beta subunit. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):155–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00374974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G. Simplified gene nomenclature. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):26–26. doi: 10.1038/352026b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Schrager P., Ritchie J. M. Neuronal-type Na+ and K+ channels in rabbit cultured Schwann cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):156–157. doi: 10.1038/311156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Dos Santos G., Pinto-Henrique D., Koulakoff A., Gros F., Berwald-Netter Y. The glial voltage-gated sodium channel: cell- and tissue-specific mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7272–7276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T., Chiu S. Y., Bevan S., Ritchie J. M. Ion channels in rabbit cultured fibroblasts. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Feb 22;227(1246):1–16. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Clevinger E. C., O'Neill T. J., Yarowsky P. J., Krueger B. K. Mutually exclusive exon splicing of type III brain sodium channel alpha subunit RNA generates developmentally regulated isoforms in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18648–18653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Ritchie J. M. Multiple kinetic components of sodium channel inactivation in rabbit Schwann cells. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:529–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Ritchie J. M. Sodium currents in Schwann cells from myelinated and non-myelinated nerves of neonatal and adult rabbits. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:169–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman R., Banker G., Steward O. Subcellular distribution of rRNA and poly(A) RNA in hippocampal neurons in culture. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Dec;20(4):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90057-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombet A., Lazdunski M. Characterization, solubilization, affinity labeling and purification of the cardiac Na+ channel using Tityus toxin gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):651–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel G. Tissue-specific expression of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel. J Membr Biol. 1992 Feb;125(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00236433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Black J. A., Waxman S. G. The expression of rat brain voltage-sensitive Na+ channel mRNAs in astrocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Apr;23(1-2):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rang H. P. Extraneuronal saxitoxin binding sites in rabbit myelinated nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarao R., Gupta S. K., Auld V. J., Dunn R. J. Developmentally regulated alternative RNA splicing of rat brain sodium channel mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5673–5679. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K. L., Krzemien D. M., McKenna N. M., Caldwell J. H. Alternatively spliced sodium channel transcripts in brain and muscle. J Neurosci. 1992 Apr;12(4):1370–1381. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-04-01370.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P., Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M. Voltage-dependent sodium and potassium channels in mammalian cultured Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):948–952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Black J. A., Ransom B. R., Waxman S. G. Ion channels in spinal cord astrocytes in vitro. I. Transient expression of high levels of Na+ and K+ channels. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Oct;68(4):985–1000. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.4.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Minturn J. E., Black J. A., Ransom B. R., Waxman S. G. Two types of Na(+)-currents in cultured rat optic nerve astrocytes: changes with time in culture and with age of culture derivation. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Oct;30(2):275–287. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490300202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Ransom B. R., Cornell-Bell A. H., Black J. A., Waxman S. G. Na(+)-current expression in rat hippocampal astrocytes in vitro: alterations during development. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jan;65(1):3–19. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.65.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Trotter J., Schachner M., Kettenmann H. Channel expression correlates with differentiation stage during the development of oligodendrocytes from their precursor cells in culture. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1135–1145. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Waxman S. G. Ion channels in spinal cord astrocytes in vitro. II. Biophysical and pharmacological analysis of two Na+ current types. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Oct;68(4):1001–1011. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.4.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhäuser C., Berger T., Frotscher M., Kettenmann H. Heterogeneity in the Membrane Current Pattern of Identified Glial Cells in the Hippocampal Slice. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(6):472–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward O., Banker G. A. Getting the message from the gene to the synapse: sorting and intracellular transport of RNA in neurons. Trends Neurosci. 1992 May;15(5):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90170-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau A., Perbal B. Several mRNAs with variable 3' untranslated regions and different stability encode the human PR264/SC35 splicing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):932–936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Sontheimer H., Black J. A., Minturn J. E., Ransom B. R. Dynamic aspects of sodium channel expression in astrocytes. Adv Neurol. 1993;59:135–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]