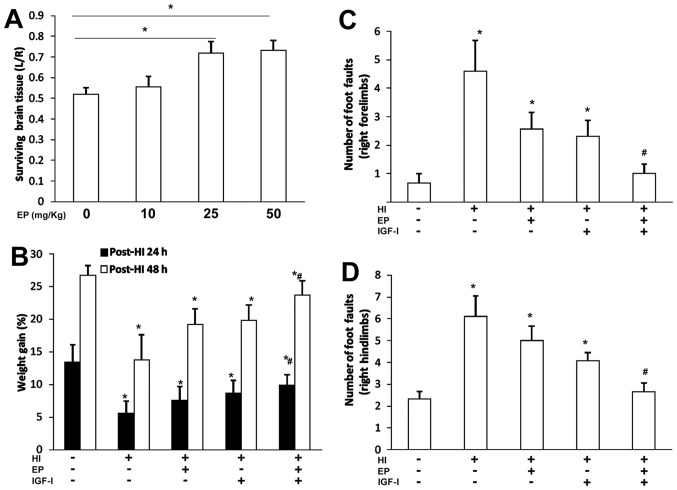
Figure 2.
Ethyl pyruvate (EP) and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) promote long-term behavioral development following hypoxic-ischemic (HI) injury. (A) EP exerted neuroprotective effects in a dose-dependent manner (30 min after HI injury) *P<0.05 as indicated (n=6). (B) Body weight following HI injury. Rat pups were treated with EP 30 min after HI injury or with IGF-I 24 h after HI injury or with both agents. The y-axis represents the percentage changes in body weight as compared to the weight before HI injury. *P<0.05 compared with the sham-operated group, #P<0.05 compared with other the 3 groups subjected to HI injury (n=8). Foot fault tests were performed at 4 weeks of recovery (P35). Number of foot faults of (C) right forelimbs or (D) right hindlimbs per 50 steps were counted within 5 min. *P<0.05 compared with sham-operated group, #P<0.05 compared with other 3 groups subjected to HI injury (n=8). L, left; R, right.