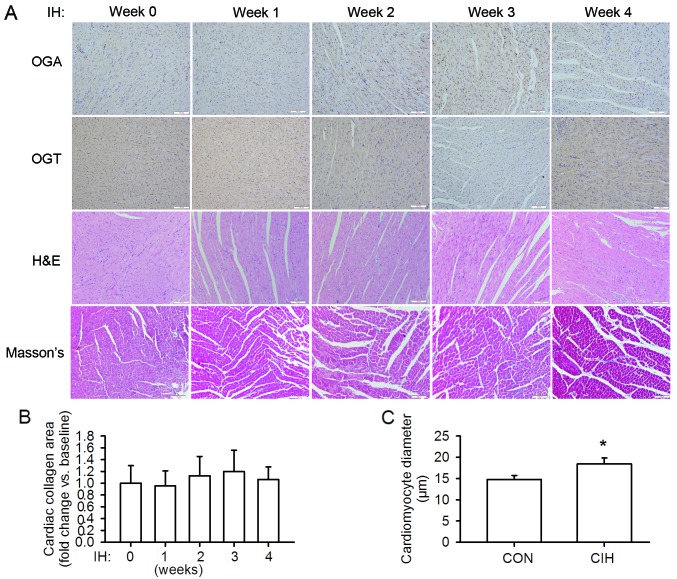
Figure 2.
Changes in cardiac architecture and protein expression during the 4 weeks of exposure to intermittent hypoxia (IH). (A) Histopathological analysis and expression of O-GlcNAcase (OGA) and O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) in the left ventricular tissues. Gradually abnormal myocardial architecture occurred due to exposure to IH, as evidenced by cardiomyocyte disarray and structural disorganization, without significant changes in collagen deposition. OGA and OGT levels changed dynamically during the 4 weeks of exposure to IH. (B) The area of cardiac interstitial collagen prior to exposure to IH was regarded as the baseline value. (C) After 4 weeks of exposure to IH (CIH) there was a significant increase in cardiomyocyte size compared with exposure to normoxia (CON). Scale bar, 100 µm. *P<0.05 vs. normoxia group.