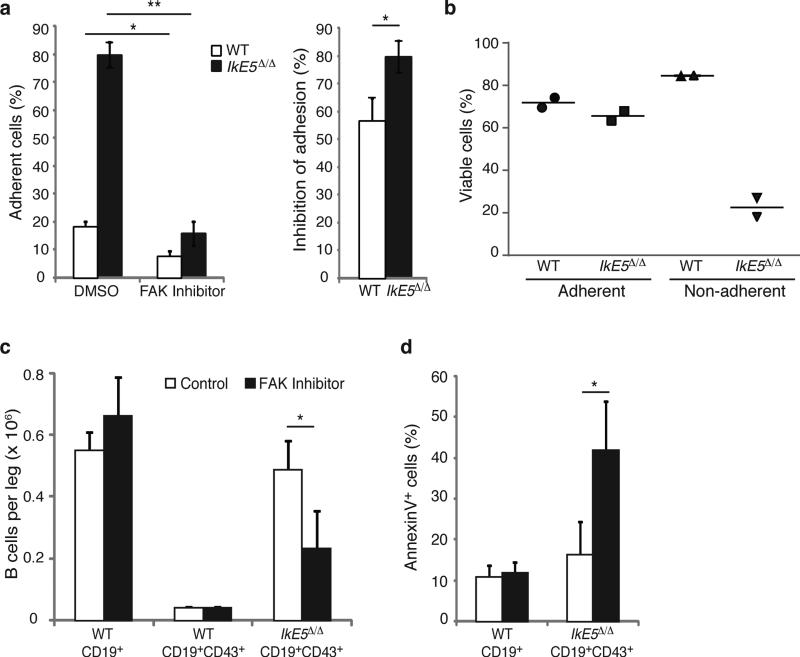
Figure 6. FAK inhibition interferes with survival of IkE5Δ/Δ pre-B cells.
a-b. In vitro effects of FAK inhibition on pre-B cell stromal adhesion and survival. The mean percentage ± s.d. of adherent cells (left) and % inhibition of adhesion ± s.d. (right), are shown in (a). The percentage of viable adherent and non-adherent cells recovered in the presence of FAK inhibitor is shown in (b). The data in (a) are from two independent cultures with replicate testing (n=4). For Annexin staining described in (b) replicates were pooled. c-d, In vivo effect of FAK inhibition on IkE5Δ/Δlarge pre-B cells. c, The mean number ± s.d. of pro-B-large pre-B cells (CD19+CD43+) per leg (femur + tibia) of WT (n=2) and IkE5Δ/Δ CD19-Cre (n=3) mice is shown after 3-5 doses of FAK inhibitor (WT, n=3; IkE5Δ/Δ CD19-Cre, n=6) or vehicle control (WT, n=2; IkE5Δ/Δ CD19-Cre, n=3). The effect of FAK inhibitor treatment on total BM B cells (CD19+) in WT mice is also shown. d, Percent of apoptotic cells (mean ± s.d.) of BM cells from panel c. Asterisks in a, c, and d denote significant changes in adhesion, cellularity or survival of WT and mutant large pre-B cells in the presence of the FAK inhibitor vs. control (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P <0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test).