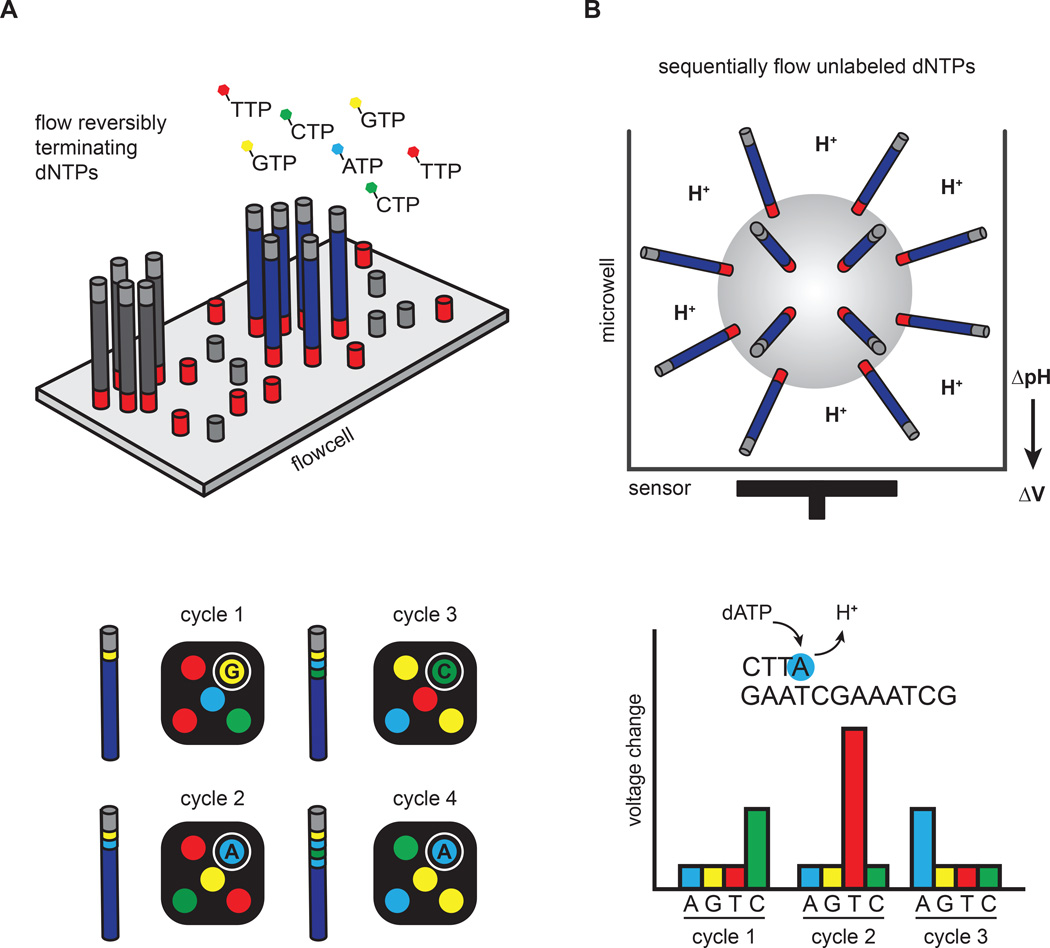
Figure 2. Clonal amplification-based sequencing platforms.
(A) Illumina’s four-color reversible termination sequencing method. DNA templates are first clonally amplified on the surface of a glass flow cell. Sequencing occurs via successive rounds of base incorporation, washing and imaging. A cleavage step after image acquisition removes the fluorescent dye and regenerates the 3´OH for the next cycle. Analysis of four-color images is used to determine base composition. (B) Ion Torrent’s semiconductor sequencing method. Emulsion-PCR is used to clonally amplify DNA templates on the surface of beads, which are subsequently placed into microwells. pH changes induced by the release of hydrogen ions during DNA extension are detected by a sensor positioned at the bottom of the microwell. These pH changes are converted into a voltage signal, which is proportional to the number of nucleotides added by the polymerase.