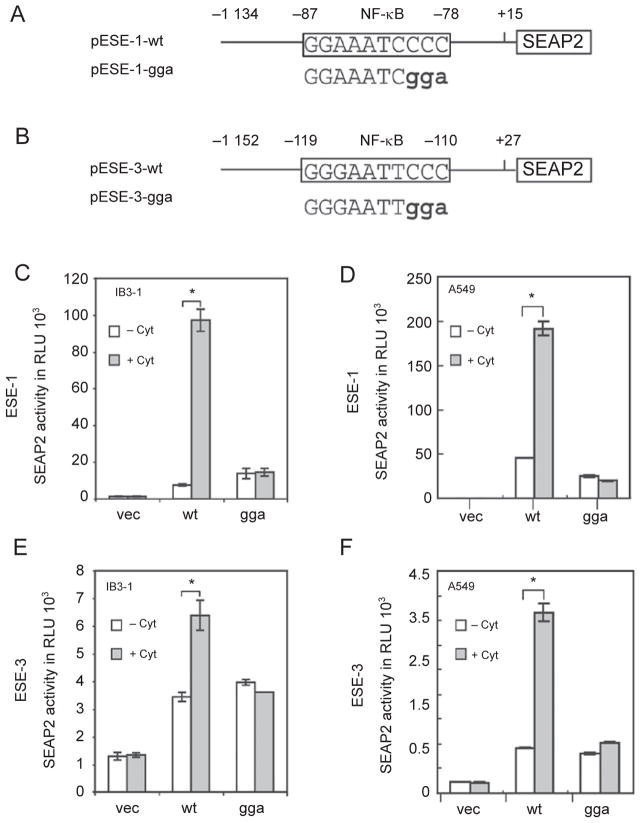
Figure 2.
Involvement of NF-κB in cytokine-induced ESE-1 and ESE-3 expression. (A, B) Schematic diagrams of human ESE-1 and ESE-3 promoter SEAP2 reporter plasmids. The NF-κB binding sites that were analyzed are shown in the rectangle and the mutants that were introduced by PCR are shown as bold characters. (C–F) Transactivation of the ESE-1 and ESE-3 promoters by cytokines and requirement of the NF-κB binding site for transactivation. IB3-1 or A459 cells were transfected with 1.5 μg promoter-SEAP reporter plasmid containing either the vector alone or wild-type (wt) or mutated (gga) NF-κB sites for 24 h. The media were changed and the cells were then stimulated with IL-1β and TNF-α (at 10 ng/ml each) for 24 h. SEAP activity was measured as relative light units by a luminometer. Values shown are the mean ± SEM (n = 3) from one representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.