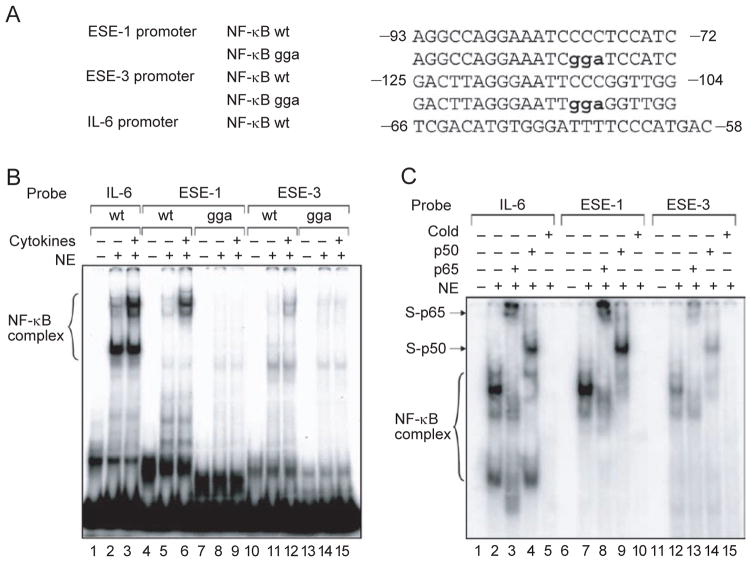
Figure 3.
Binding of NF-κB to the ESE-1 and ESE-3 promoters. (A) Putative NF-κB binding sites (wt) and their mutants (gga) in human ESE-1 and ESE-3 promoters were analyzed in electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA), using the NF-κB site on the IL-6 promoter as a positive control. (B) EMSA using oligonucleotide probes containing the indicated NF-κB sites (wt or gga) with 5 μg nuclear extract from BEAS-2B cells stimulated with IL-1β and TNF-α (at 10 ng/ml each) for 2 h, or nuclear extract from unstimulated cells. Brackets indicate the specific cytokine-inducible DNA-protein complexes.(C) Supershift and competition assays. Antibodies against the NF-κB subunits p65 and p50 were used to determine the specificity of their binding complexes. Arrows indicate supershift bands with the p65 or p50 subunits, ‘cold’ indicates competition with 500-fold of unlabelled probe.