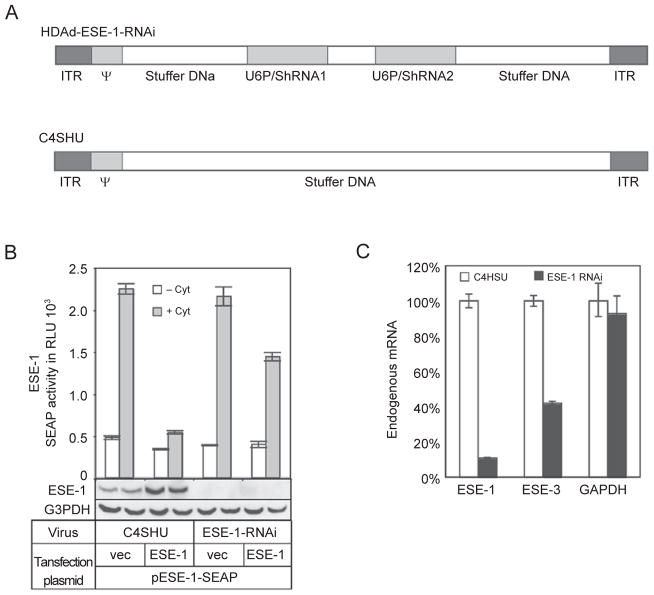
Figure 6.
Effects of knocking down ESE-1 expression on ESE-1 promoter activity and endogenous ESE-3 expression. (A) Schematic diagrams of helper-dependent adenoviral (HDAd) vectors. HDAd-ESE-1-RNAi expresses two shRNAs from the murine U6 gene promoter. C4HSU is a control vector that does not express any transgene. ITR, inverted terminal repeat; ψ, packing signal. (B) Promoter activity analysis in ESE-1 knocked down cells. A549 cells were transduced with a control vector, C4SHU, or HDAd-ESE-1-RNAi overnight and then transfected and stimulated as before. Inhibition of cytokine-induced ESE-1 promoter activity by ESE-1 overexpression was partially relieved when ESE-1 was knocked down by HDAd-ESE-1-RNAi. ESE-1 expression (endogenous and/or exogenous) was undetectable when cells were transduced with HDAd-ESE-1-RNAi as shown using the western blotting technique. (C) Endogenous ESE-1 regulates constitutive ESE-3 gene expression. Cells were collected 3 days after virus transduction. Relative mRNA levels were calculated after normalizing to 18S using real-time RT-PCR. Data shown are the mean ± SD (n = 3) from one representative of three independent experiments.