Figure 5. JNK2 increases putative tumor initiating cells and inhibits ER expression in p53ko mouse and mutant p53-expressing human cells.
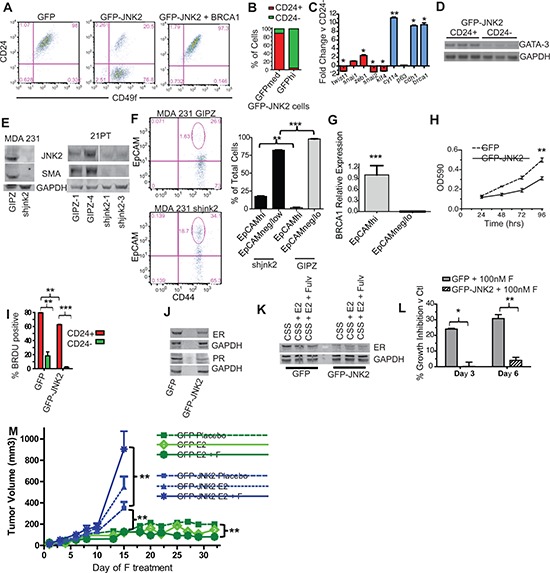
A. CD24/CD49f staining was compared in p53ko cell lines by flow cytometry; B. The percentage of CD24− and CD24+ cells were assessed in p53ko;jnk2ko GFP-JNK2 cells that were gated for GFP expression (medium and high) by flow cytometry; C. CD24+ and CD24− populations in p53ko;jnk2ko GFP-JNK2 cells were separated by FACS and expression of EMT/stem (red) and differentiation (blue) markers measured by qPCR; D. CD24+ and CD24- populations in p53ko;jnk2ko GFP-JNK2 cells were tested for Gata-3 expression by RT-PCR; E. shJNK2 or GIPZ non-silencing plasmids were stably expressed in mutant p53-expressing MDA 231 and 21PT cell lines. JNK2 and SMA expression were measured by western blot; F. MDA 231 cells were assessed for EpCAM and CD44 expression; G. EpCAMhi and EpCAMneg/lo populations in MDA 231 cells were separated by FACS. Brca1 was measured by qPCR; H. Cell viability of p53ko cells was evaluated using MTT assay; I. p53ko cells were pulse labeled with BrdU. BrdU incorporation in CD24+ and CD24− populations was measured; J. Western blot of ER and PR expression in p53ko cells; K. p53ko cells were cultured with charcoal stripped serum (CSS), CSS + Estradiol (E2), or CSS + E2 + Fulvestrant (F) and ER expression was measured by western blot; L. p53ko cells were cultured in full medium with or without F. Cell viability was measured at times indicated. Suppression of growth is shown as percentage of DMSO control growth for each genotype; M. Effect of E2 and E2-F treatment on orthotopically growing p53ko;jnk2ko GFP and GFP-JNK2 cells.
