Figure 4. Inhibition of IMPDH2 leads to nucleolar instability, p53 activation and upregulation of MYC-targeting miRs.
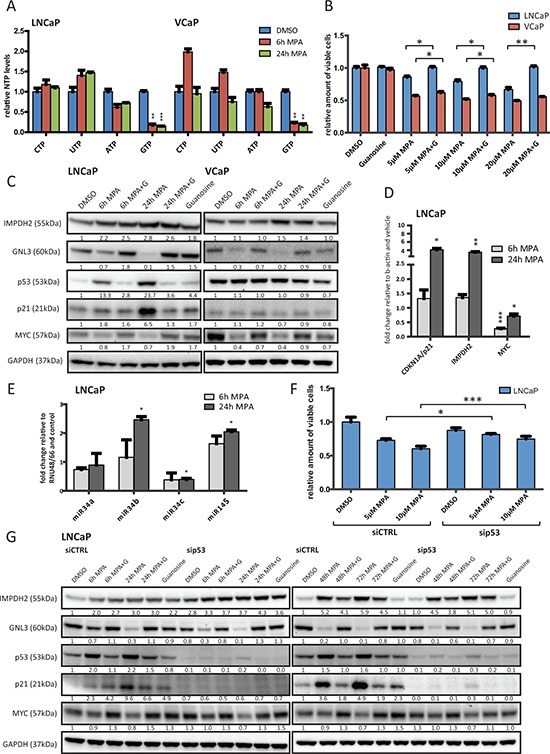
A. HPLC results of cellular nucleoside triphosphate levels. LNCaP and VCaP cells were treated with 10 μM MPA for the indicated time points, lysed and subjected to HPLC to detect cellular levels of presented nucleoside triphosphates (NTP). Values were normalized to DMSO treated cells and protein content. n = 3 B. Cell viability results of MPA treated cells. Cells were allowed to attach for 48 h prior to treatment with indicated doses of MPA and guanosine (100 μM) for 72 h. Cell viability relative to vehicle control was determined using a MTS-based assay. n = 3 C. Western blot results of MPA treated PCa cells. LNCaP and VCaP cells were treated with 10 μM MPA and 100 μM guanosine (G) for the indicated time points. Protein extracts were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis using the indicated primary antibodies. Protein levels were normalized to DMSO controls and GAPDH levels. D. Real-time PCR results. LNCaP cells were treated with 10 μM MPA for the indicated time points. Total RNA was isolated, reverse transcribed and used for qRT-PCR. n = 3 E. miRNA detection using real-time PCR of MPA treated LNCaP. Cells were treated with 10 μM MPA for the indicated time points prior to total RNA isolation using Trizol reagent and miR-detection using TaqMan assays. n = 2 F. Cell viability results of siRNA and MPA treated cells. Cells were transfected with 50 nM control or p53 siRNA for 48 h. Following treatment with the indicated drugs for another 72 h, viability was assessed using a MTS-based assay. n = 3 G. Western Blot results of siRNA and MPA treated LNCaP. Cells were transfected with 50 nM control or p53 siRNA for 48 h and then treated with 10 μM MPA and 100 μM guanosine (G) for the indicated time points. Protein lysates were harvested, separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted for the indicated proteins.
