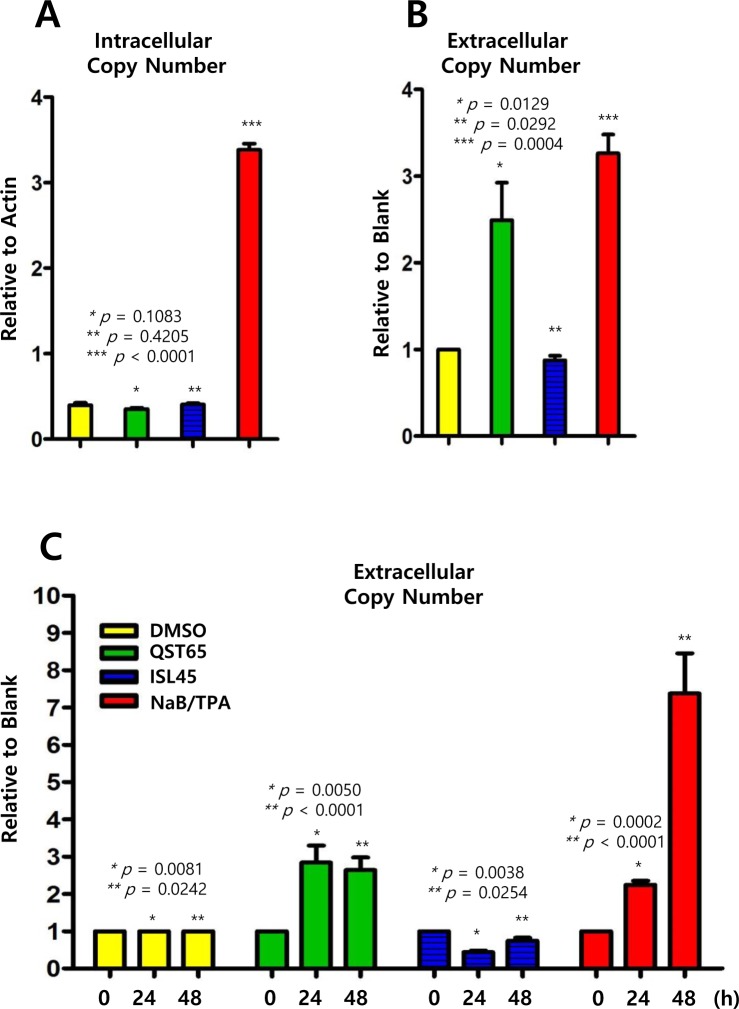
Figure 10. Effects of quercetin or isoliquiritigenin on EBV progeny production.
Intracellular and extracellular EBV genome copy numbers in SNU719 cells were determined by following methods previously described to evaluate antiviral effects of quercetin and isoliquritingenin on EBV progeny production. (A) Compared to DMSO treatment (negative control), EBV intracellular copy numbers were not changed by treatments of quercetin (62 μM) or isoliquiritigenin (45 μM). (B) Compared to DMSO treatment (negative control), EBV extracellular copy numbers were remarkably increased by quercetin treatment, while the copy numers were not affected by isoliquiritigenin. Intracellular and extracellular copy numbers were calculated as relative intracellular (relative to Actin) and extracellular (relative to blank treatment) EBV genome copy numbers, respectively. Statistical significance is when the P-value is < 0.05 (95% confidence). NaB/TPA treatment stands for 1 mM treatment of NaB and 1 ng/ml treatment of TPA. ISL and QST stands for isoliquiritigenin and quercetin, respectively. (C) Time kinetics of effects of quercetin and isoliquritigenin on EBV progeny production in SNU719 cells. During 48 h time course, quercetin treatment showed to significantly enhance EBV progency production since 24 h post treatment. DMSO, QST62, ISL45, and TPA/NaB stand for DMSO treatment, 62 μM isoliquiritigenin treatment, 45 μM quercetin treatment, and TPA (20 ng/mL) and NaB (3 mM) co-treatment, respectively.