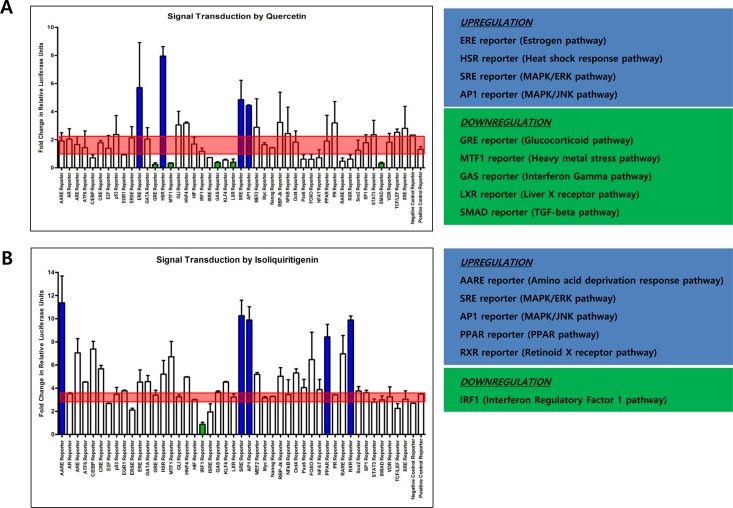
Figure 5. Effects of quercetin or isoliquiritigenin on signal transduction.
Cignal finder reporter assay was conducted to determine what signaling pathways inSNU719 cells are affected by treatments of quercetin or isoliquiritigenin. SNU719 cells were treated 62 μM quercetin or 45 μM isoliquiritigenin for 48 h and subjected to Cignal finder reporter assay. Each reporter is a luciferase construct in which a transcriptional factor specific to a signaling pathway was cloned. Signaling pathways affected by either quercetin or isoliquiritigenin were chosen when their fold changes were immensely higher or lower than negative and positive reporter signals (shaded by red box). Reporters induced by either quercetin or isoliquiritigenin were in blue box and reporters suppressed by either quercetin or isoliquiritigenin were in green box. ERE, HSR, SRE, AP1 reporters were upregulated by quercetin, and these reporters are specific to estrogen pathway, heat shock response pathway, MAPK/ERK pathway and MARK/JNK pathway, respectively. GRE, MTF1, GAS, LXR, SMAD reporters were downregulated by quercetin, and these reporters are specific to glucocorticoid pathway, heavy metal stress pathway, interferon gamma pathway, liver X receptor pathway and TGF-beta pathway, respectively. AARE, SRE, AP1, PPAR, RXR reporters were upregulated by isoliquiritigenin, and these reporters are specific to amino acid deprivation response pathway, MAPK/ERK pathway, MAPK/JNK pathway, PPAR pathway and retinoid X receptor pathway, respectively. IFR1 reporter was downregulated by isoliquiritigenin and this reporter is specific to interferon regulatory factor 1 pathway.