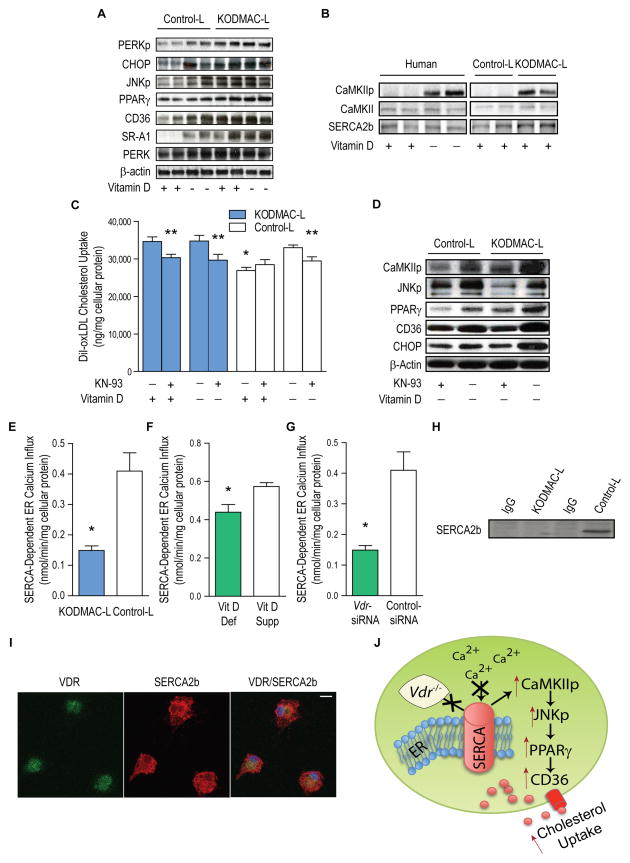
Figure 4. Deletion of macrophage Vdr increased ER stress and accelerated cholesterol uptake by activation of the CaMKII signaling pathway.
Peritoneal macrophages from KODMAC-L or control-L before HFD and/or human monocyte-derived macrophages from type 2 diabetics were cultured for 5 d in vitamin D-deficient or 1,25(OH)2D3-supplemented conditions. (A) Western blot of ER stress and cholesterol signaling proteins). (B) Western blot of SERCA2b and CaMKII activation (representative of n=4 per group), (C) Cholesterol uptake after DiI-oxLDL stimulation in murine macrophages with or without CaMKII inhibitor KN-93 for 6 h (n=7 per group) (*P<0.001 by ANOVA vs. all others without KN-93, **P<0.05 vs. same cells without KN-93). (D) Western blot of activated CaMKII and JNK, PPARγ, CD36, and ER stress protein CHOP in murine macrophages with or without KN-93 (representative of n=4 per group). SERCA2b activity from (E) murine macrophages cultured in 1,25(OH)2D3-supplemented media (n=4 per group), (F) human macrophages cultured in vitamin D-deficient or 1,25(OH)2D3-supplemented conditions (n=5 per group), and (G) human macrophages cultured in 1,25(OH)2D3-supplemented conditions and infected with Vdr-siRNA or control siRNA (n=5 per group) (*P<0.05 vs. control-L or vitamin D-supplemented for all). (H) SERCA2b expression in murine control-L macrophage lysates immunoprecipitated with VDR antibody and (I) Immunofluorescent staining for VDR (green, left), SERCA2b (red, middle), and co-localization (yellow, right) in murine control-L macrophages. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (J) Schematic depicting VDR-driven modulation of SERCA2b activity and induction of foam cell formation. Data expressed as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.