Fig. 5.
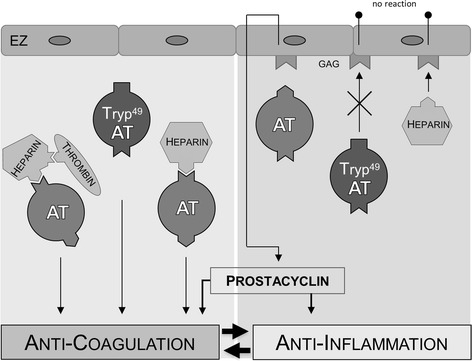
Function of antithrombin. Schematic overview of the anticoagulant function of antithrombin (AT) and the mediation of anti-inflammation through glycosaminoglycan (GAG) binding at the endothelial cell (EC) with subsequent release of prostacyclin (PGI2). Until now, it was not clarified whether the antithrombotic potency of AT is exclusively based on its solitary anticoagulant capacity or if it might also depend on its anti-inflammatory mode of action. The data in the here-presented study indicates that the anti-inflammatory property of AT is a prerequisite for mediating adequate anticoagulation
