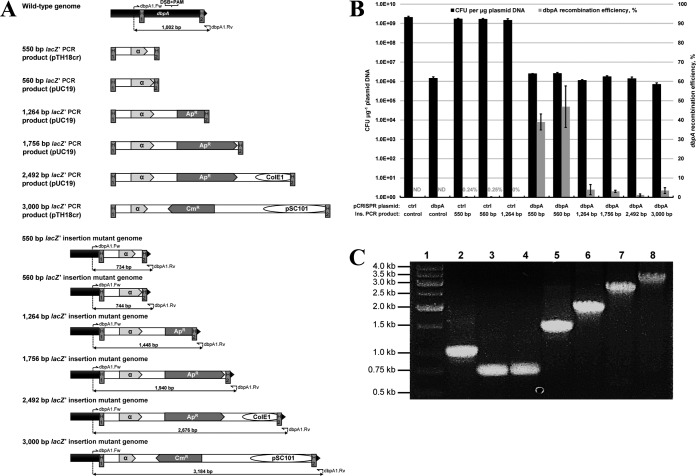
FIG 4.
Challenging the proposed strategy of dsDNA gene replacement by varying dsDNA insertion size. (A) Replacement of an 818-bp region of the dbpA gene with recombinogenic PCR products of various sizes yielding lacZ′ (α). Products were PCR amplified from plasmid pUC19 (560-bp, 1,264-bp, 1,756-bp, and 2,492-bp products) or pTH18cr (550-bp and 3,000-bp products) using PCR primers possessing H1 and H2 homology regions. Regions corresponding to the β-lactamase (Apr) coding sequence, ColE1 RNA (ColE1), and repA coding sequence (pSC101) are truncated in the 1,264-bp, 2,492-bp, and 3,000-bp products, respectively. In each case, successful gene replacement replaces the dbpA PAM sequence and avoids creation of a chromosomal DSB, which are both located between the H1 and H2 homology regions. The expected genomic layout at the dbpA locus is shown for each gene replacement mutant. Primer binding sites and expected PCR product sizes are also depicted for each dbpA gene replacement mutant, in addition to the wild-type strain. Genes and plasmid regions corresponding to dbpA, lacZ′, Apr, Cmr, ColE1, and pSC101 sequences are depicted to scale. Note that size of the lacZ′ coding sequence differs between plasmids pUC19 (324 bp) and pTH18cr (237 bp). (B) Electroporation and dbpA recombination efficiency data resulting from electroporation (pCRISPR::ctrl plus control PCR product), CRISPR/Cas9 (pCRISPR::dbpA plus control PCR product), and recombineering (pCRISPR::ctrl plus 550-bp, 560-bp, or 1,264-bp PCR insertion cassette) controls, as well as six various-size chromosomal deletions using CRISPR/Cas9-coupled recombineering (pCRISPR::dbpA plus PCR insertion cassette). Electroporation efficiency is defined as the total number of CFU generated per microgram of plasmid DNA (pCRISPR::ctrl or pCRISPR::dbpA), and dbpA recombination efficiency was measured by determining the proportion of blue colonies. A recombination efficiency of 0% reflects an inability to identify blue mutant colonies on agar plates containing up to 400 transformants. Recombination efficiency at the dbpA locus was not determined (ND) for electroporation of the nonrecombinogenic control PCR product. Results shown are averages of at least two independent experiments, and error bars depict standard deviations. (C) Colony PCR screening of dbpA gene replacement mutants. Primers dbpA1.Fw and dbpA1.Rv were utilized in a colony PCR with one blue colony resulting from each gene replacement scheme. Lane 1, marker; lane 2, wild-type E. coli colony; lane 3, 550-bp insertional colony; lane 4, 560-bp insertional colony; lane 5, 1,264-bp insertional colony; lane 6, 1,756-bp insertional colony; lane 7, 2,492-bp insertional colony; lane 8, 3,000-bp insertional colony.