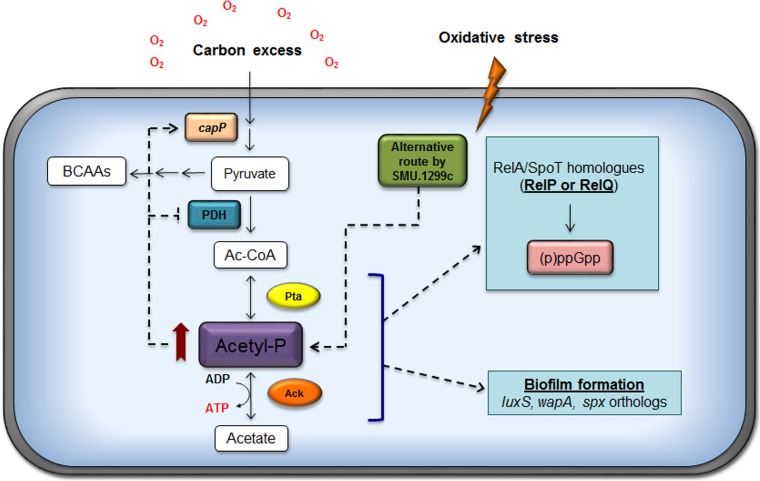
FIG 7.
Current model for the role of the Pta-Ack pathway in S. mutans. The activities of products encoded by the ackA or pta genes are primarily responsible for the generation of AcP, the levels of which strongly influence physiology and gene expression in S. mutans. In particular, the role of the Pta-Ack pathway in modulating the expression of genes involved in carbohydrate flux at the pyruvate node, as well as those contributing to biofilm formation and stress tolerance, is significant. Moreover, a metabolic linkage between acetate metabolism and (p)ppGpp production in response to oxidative stress is established and is probably mediated by the small (p)ppGpp synthase RelP and the two-component signal transduction system RelRS. Red arrow, high level of accumulation of AcP; dashed arrows, the observations and models.