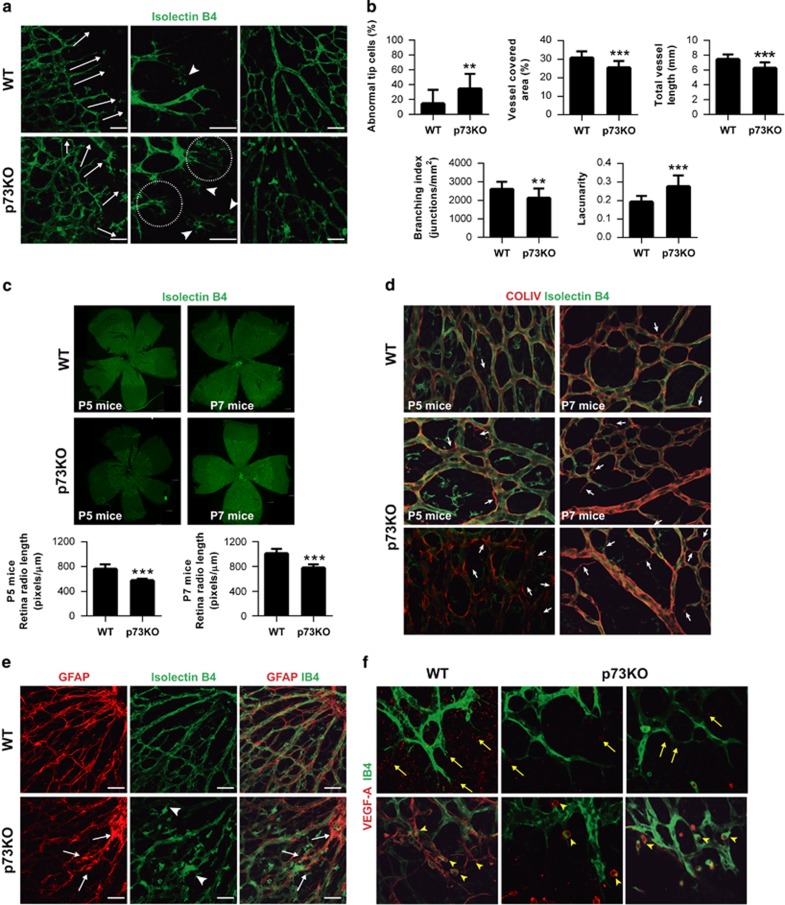
Figure 1.
Absence of p73 perturbs development of the retinal vasculature. (a) Retinas from P5 WT and p73KO mice were stained with isolectin B4 (IB4) to analyze the morphology and orientation (white arrows, left panels) of filopodia at the leading edge of vascularization. Higher-magnification images for each genotype (medium panels) show abundant and disorientated filopodia (circles) and tissue macrophages (arrow heads) in p73KO retinas. Scale bars=50 μm. Right panels illustrate perturbed vascular branching and decreased vascular density in p73KO central retinal plexus compared with WT. (b) Quantification of vessel coverage (percentage of area covered by IB4+ endothelial cells), total vessel length, vascular branching index (branch points/unit area) and lacunarity (distribution of the gap sizes surrounding the object). Representative images were analyzed independently using the AngioTool software (https://ccrod.cancer.gov/confluence/display/ROB2/Home). (c) IB4 retinal flat-mount staining of P5 and P7 retinas. Radio was measured from the optic nerve to the sprouting zone. The spreading of the vasculature toward the periphery is highly significantly reduced in p73KO retinas. (d) Visualization of empty matrix sleeves by IB4 (green) and collagen IV (red) staining, with increased presence of collagen IV sleeve segments lacking endothelial cells (IB4-negative; white arrows) in p73KO retinas. (e) GFAP/IB4 double staining to visualize astrocytes (red) and vasculature (green), respectively. p73KO retinas display a disorganized astrocyte network underlying a chaotic vasculature; tufts are indicated by arrow heads. (f) VEGF-A immunostaining (red) in P5 retinas. Note that VEGF-A expression is markedly decreased in the absence of p73. Yellow arrow heads indicate IB4+/VEGF-A+ microglial cells commonly found at sites of prospective sprout anastomosis. All statistical analysis were performed with data from at least five animals. Bar graphs represent mean±S.D. Equal-variance Student's t-test was performed to evaluate statistical differences. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001