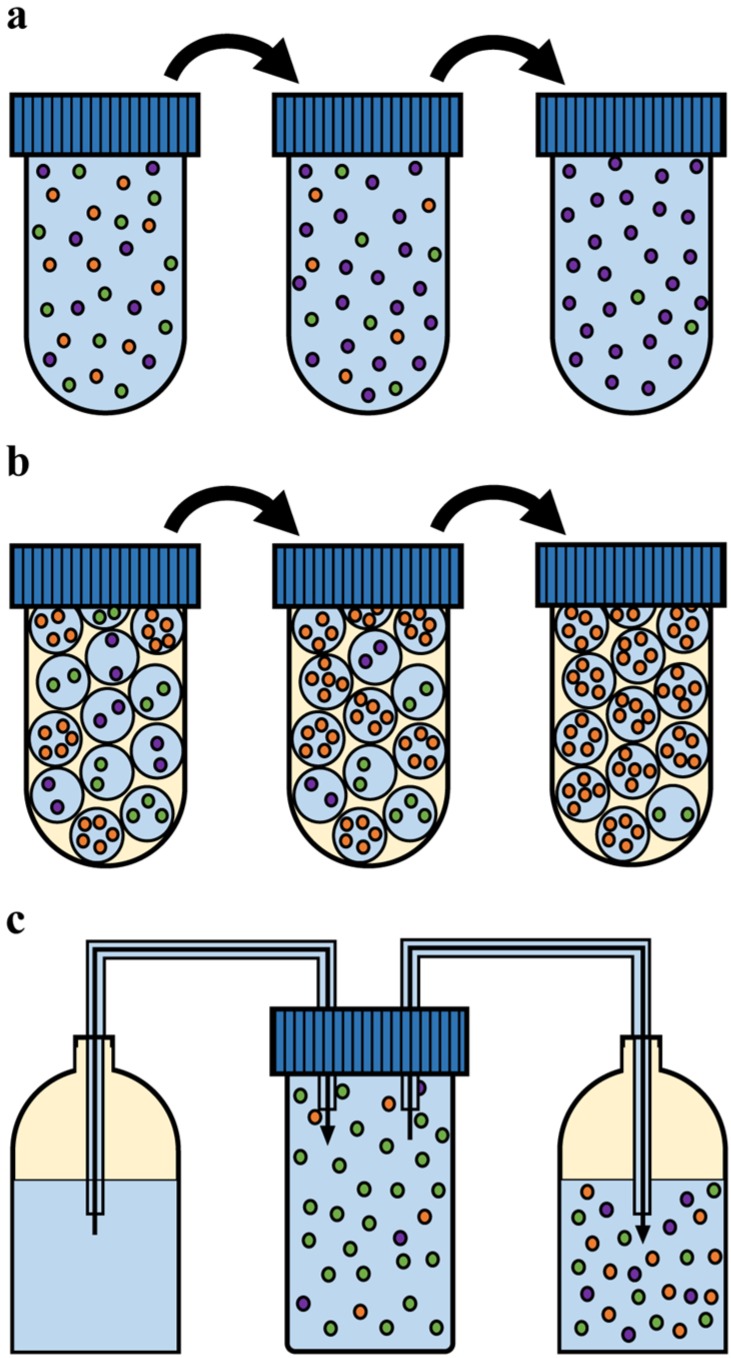
Figure 4.
Culturing methods used in laboratory evolution experiments. (a) Serial propagation in batch, where after a certain period of growth in suspension, cells are diluted into fresh medium and the cycle is repeated; (b) Serial propagation in emulsion, where single cells are compartmentalized in a water-in-oil emulsion, thereby privatizing the resources. Each cell is now allowed to deplete the resources before the cells are mixed, diluted and a new emulsion is made. This cycle is subsequently repeated; (c) During chemostat culturing, a continuous inflow and outflow of medium ensure constant growth rate and conditions for the cell population. In all figures the different colours indicate different genotypes.