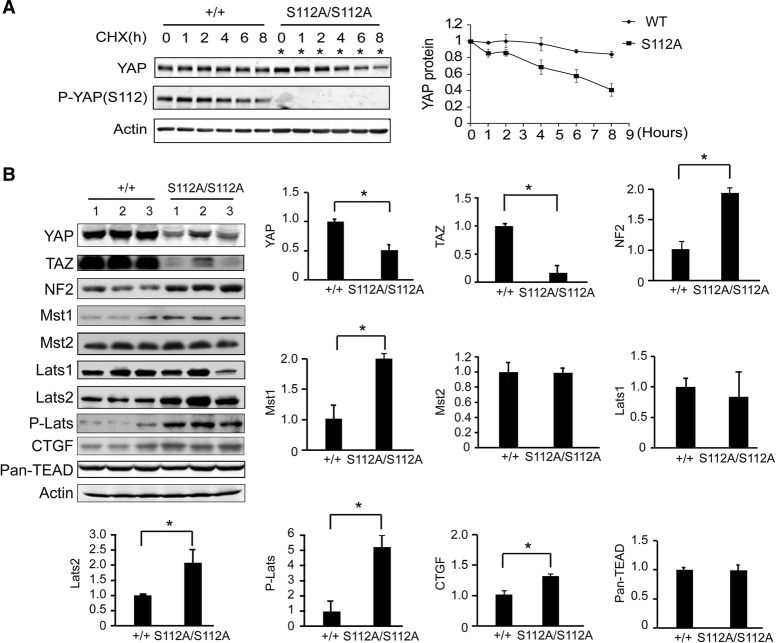
Figure 6.
Compensatory decrease of YAP stability and activation of the Hippo kinase cascade in the YapS112A mice. (A) Faster turnover of endogenous YAPS112A protein compared with endogenous wild-type (WT) YAP protein. Confluent cultures of wild-type and YapS112A MEFs were treated with 50 µg/mL CHX for different periods of time and probed with the indicated antibodies. A representative blot is shown. YAP protein levels were quantified by the LI-COR Odyssey imaging system from three parallel experiments, normalized to actin, and arbitrarily set as 1 at time 0 in the graph shown at the right. Note that twice as much YapS112A cell lysates were loaded in each lane to adjust for the lower levels of YAP protein in the YapS112A cells (*). (B) Western blot analysis of liver protein lysates from wild-type and YapS112A mice. The graphs show quantification of YAP, TAZ, NF2, Mst1, Mst2, Lats1, Lats2, p-Lats, TEAD1-4, and CTGF levels in mutant livers relative to wild-type livers. Data are mean ± SD from three animals for each genotype. (*) P < 0.05, t-test.