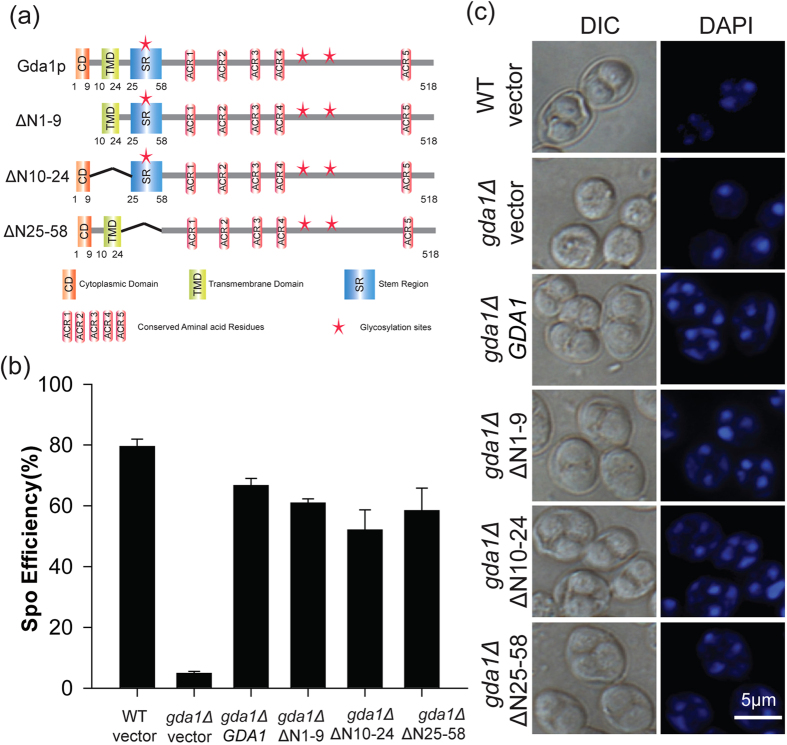
Figure 4. N-terminal domains of Gda1p are not necessary for its role in meiosis.
(a) Schematic representation of the domains of Gda1p and some mutants, including ΔN1–9 (Δ1–9aa), ΔN10–24 (Δ10–24aa), and ΔN25–58 (Δ25–58aa). CD indicates the cytoplasmic domain; TMD indicates the transmembrane domain; SR indicates the stem region; ACR1–5 indicates the conserved amino acids related to guanosine diphosphatase activity; stars indicate the glycosylation sites. (b) The function of GDA1 in meiosis was independent of its localization-terminal domains. The WT strain harboring the empty vector and the gda1Δ strains harboring either the empty vector or GDA1, ΔN1–9, ΔN10–24, ΔN25–58 under the control of its own promoter were incubated in sporulation medium for 24 hrs. Sporulation efficiency was determined by staining with DAPI. (c) Microscopic observation of the WT strain harboring the empty vector and the gda1Δ strains harboring either the empty vector or GDA1 and its variants under the control of its own promoter after sporulation induction for 24 hrs.