Figure 6. The function of Gda1p in entering the pre-meiotic S phase is dependent on its guanosine diphosphatase activity.
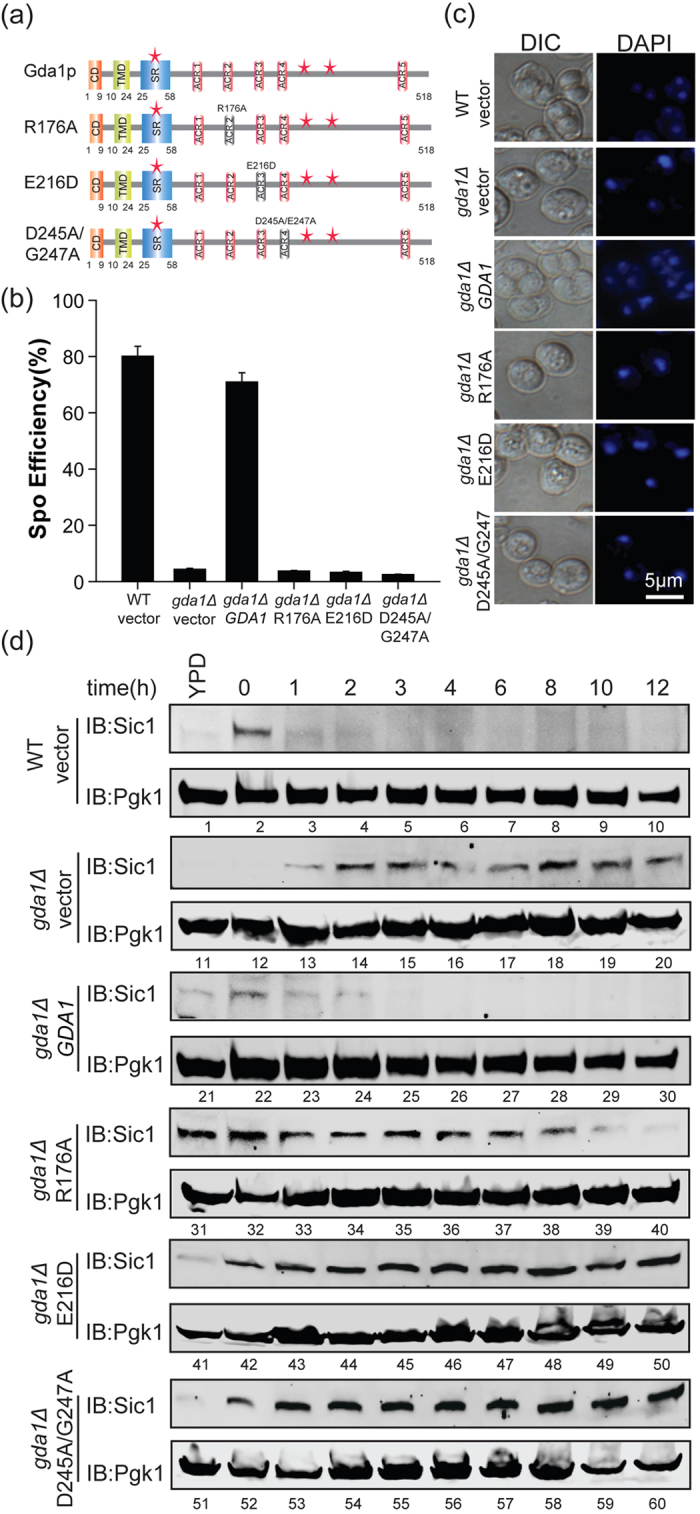
(a) Schematic representation of the key guanosine diphosphatase activity mutants, which include GDA1 (Gda1p 1–518aa), R176A (Gda1p R176A), E216D (Gda1p E216D), and D245A/G247A (Gda1p D245A/G247A). (b) The disruption of Gda1p guanosine diphosphatase activity induced a decrease in sporulation efficiency compared with the WT strain. The WT strain harboring the empty vector and the gda1Δ strains harboring either the empty vector or GDA1, R176A, E216D, D245A/G247A under the control of its own promoter were incubated in sporulation medium for 24 hrs. Sporulation efficiency was determined by staining with DAPI. (c) Microscopic observation of the WT strain harboring empty vector and the gda1Δ strains harboring either the empty vector, WT GDA1 or key guanosine diphosphatase activity mutants under the control of their own promoter after sporulation induction for 24 hrs. (d) The disruption of GDA1 guanosine diphosphatase activity stabilized Sic1p during sporulation. The WT strain harboring empty vector and the gda1Δ strains harboring either empty vector or GDA1, R176A, E216D, D245A/G247A mutants under the control of their own promoter were incubated in sporulation medium and samples were collected at different times after induction. The expression of Sic1p over time was analyzed by immunoblotting with specific anti-Sic1 antibodies. Pgk1p served as a loading control. Full-length blots/gels are presented in Supplementary Figure 5.
