Figure 2.
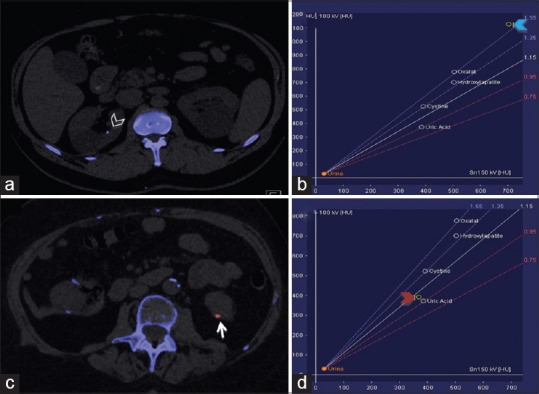
Characterization of kidney stones using dual-energy computed tomography (DECT). DECT helps to distinguish between uric acid and non-uric acid renal stones. a and c are axial images acquired from different patients who presented with flank pain. (a) Axial image showing a non-uric acid renal stone in the right kidney (arrowhead) colored in blue. (b) Graph showing the composition of this stone (blue arrowhead). (c) Axial image showing a uric acid renal calculus in the left kidney (arrow) colored in red. (d) Graph confirms the composition of the stone (red arrowhead)
