Figure 6.
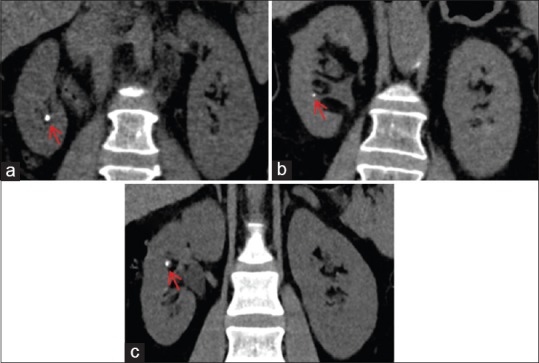
Iterative reconstruction (IR) levels in computed tomography (CT) scans performed for renal stones. IR techniques decrease image noise, allowing radiation dose reduction, while image quality is preserved or even improved. High levels of IR techniques are desired for CT scans performed for renal stones. (a–c) Coronal images from different patients generated with high levels of different IR techniques, showing renal stones in the right kidney (red arrows). (a) Image reconstructed with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction 80%; patient's weight 70 kg and CTDIvol: 3.84 mGy. (b) iDose4 L5; patient's weight 71 kg and CTDIvol: 5.66 mGy. (c) Sonogram affirmed iterative reconstruction 4; patient's weight 81 kg and CTDIvol: 8.74 mGy. Note the comparable image quality and contrast preservation among the different images, allowing the diagnosis of urolithiasis
