Figure 1.
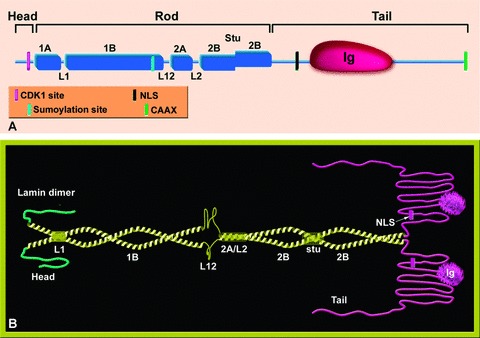
Schematic representation of the structure of lamin proteins. (A) The lamin monomer. The lamin is divided into three domains, head, rod and a globular tail. The rod domain is composed of four coiled-coil regions (1A, 1B, 2A, 2B) that are connected through three short linkers (L1, L12, L2). Marked on the scheme are the Ig globular domain in the tail and the stutter (a discontinuity of the heptad repeat) in coil 2B. Also shown by colour code are the positions of the CDK-1 recognition site (absent in Ce-lamin), the sumoylation site in human lamin A, the nuclear localization signal (NLS) and the CAAX motif. (B) A model of lamin dimers. A pair of parallel coiled-coil rods forms the lamin dimer (yellow). The non-α-helical head and tail domains are coloured green and pink, respectively. The different sub-domains are indicated. In coil 2B the stutter leads to a local unwinding.
