Figure 2. Hsp90 chaperone cycle.
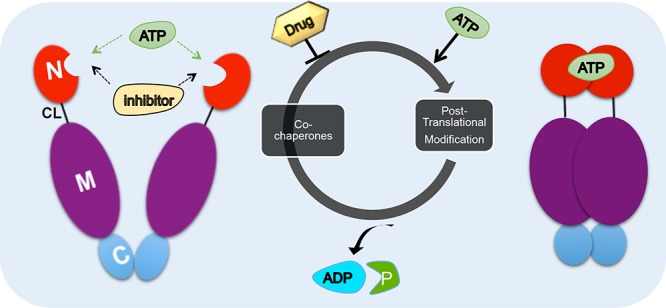
ATP binding to the N-terminal domain of Hsp90 (red) in an “open” conformation promotes transient dimerization of the N-domains “closed” conformation leading to ATP hydrolysis [38]. The co-chaperones such as Aha1, Cdc37, HOP and p23 and post-translational modification influence the rate of ATP hydrolysis. Domain labeling is as follows: N, N-domain (red); CL, charged linker (black); M, M-domain (purple); C, C-domain (blue).
