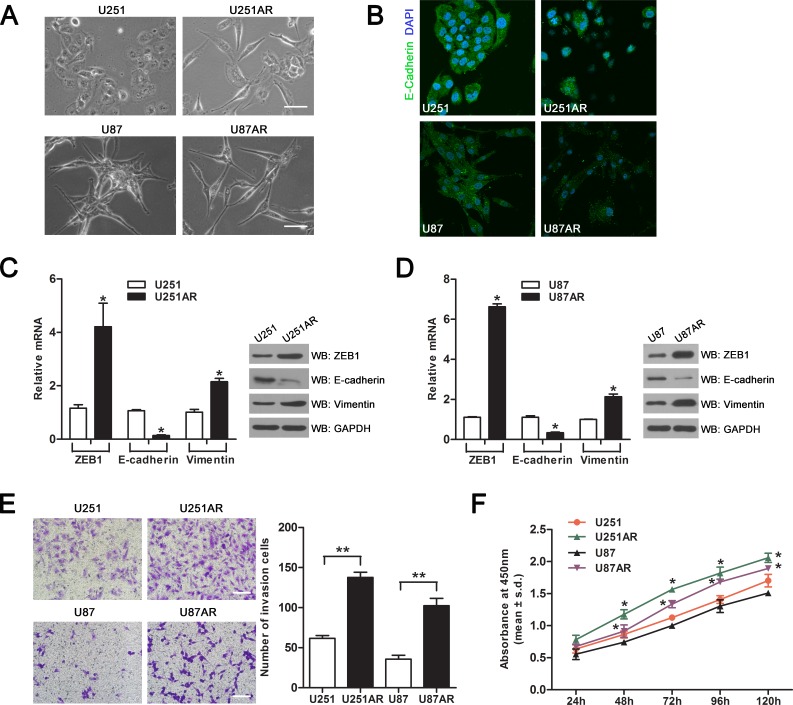
Figure 1. Imatinib-resistant U251AR and U87AR cells exhibit EMT characteristics.
(A) Morphological differences between parental cells and imatinib-resistant GBM cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of cell-cell junction protein E-cadherin. Parental and resistant GBM cells were stained with E-cadherin (green) as well as DAPI (blue) and pictures were taken at ×40 magnification. Nuclei are stained in blue with DAPI. (C) The mRNA and protein levels of EMT markers in U251 and U251AR cells were respectively detected by qRT-PCR and western blotting. (D) The mRNA and protein levels of EMT markers in U87 and U87AR cells were respectively detected by qRT-PCR and western blotting. (E) Transwell invasion assay proves an altered invasive behavior of imatinib-resistant GBM cells. Scale bar, 200 μm. (F) The cell viability of parental and resistant GBM cells after treatment with 50 μg/ml TMZ for 24, 48, 72, 96 and 120 h. Data are represented as mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. TMZ, temozolomide. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.