Figure 1. The presence of the GSK3 inhibitor, SB216763 or CHIR99021, antagonizes rapamycin's growth inhibitory effects evaluated in a 3-day monolayer culture assay (A and B), in an 8-day colony formation assay (C), by cell cycle analysis (D) and in a nude mice xenograph model (E).
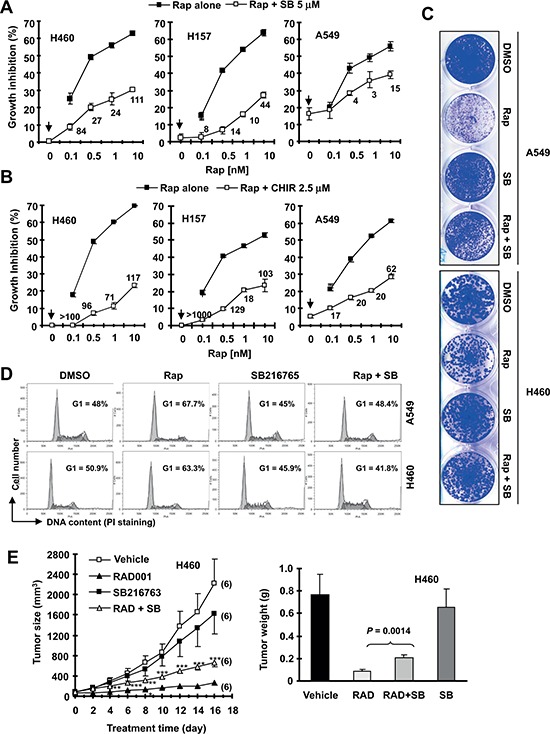
(A and B), The given lung cancer cell lines were plated on 96-well cell culture plates and treated next day with the indicated concentrations of rapamycin (Rap) alone, SB216763 (SB) or CHIR99021 (CHIR) alone (as indicated by arrow inside the graphs) or their combination. After 3 days, cell numbers were estimated using the SRB assay and CIs were calculated with CompuSyn software and labeled inside the graphs. Data, means of four replicated determinations; Bars, ± SDs. (C), The indicated cell lines at a density of approximately 400 cells/well were seeded in 12-well plates. On the second day, the cells were treated with DMSO, 10 nM rapamycin, 5 μM SB216763, or rapamycin plus SB216763 (SB). After 8 days, the plates were stained for the formation of cell colonies with crystal violet dye and pictured using a digital camera. (D), The indicated lung cancer cell lines were treated with DMSO, 10 nM rapamycin, 5 μM SB216763, or rapamycin plus SB216763 for 48 h and then harvested for cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry. (E), H460 xenografts were treated with indicated agents. This study was done in conjunction with our previous INK128 and SB216763 combination experiment and thus the vehicle and SB216763 groups were shared to minimally use mice (see details in “Materials and Methods”). Tumor sizes were measured once every two days. Each measurement is a mean ± SE (n = 6). At the end of the experiment, tumor xenografts were removed and weighed. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared with RAD001 group alone using the student t test.
