Figure 1. Blockage of autophagy enhances MLN4924-induced suppression of liver-cancer cell proliferation.
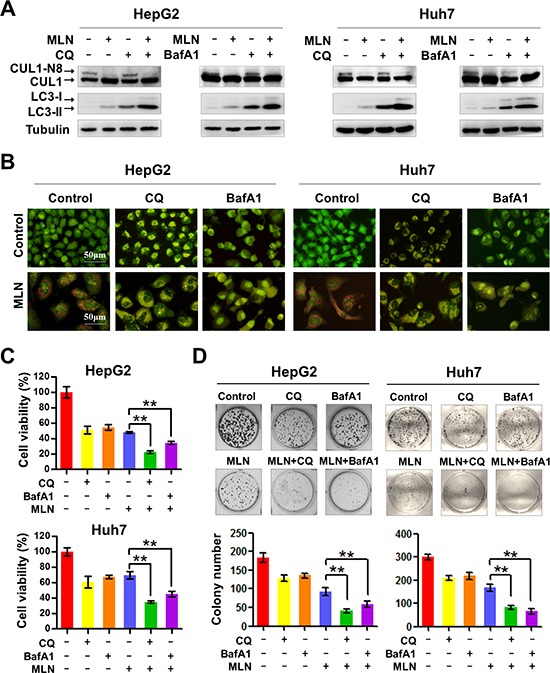
(A) Treatment with CQ or BafA1 suppressed cullin neddylation and LC3-II degradation. HepG2 and Huh7 cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to cullin1, LC3 and tubulin. Representative images of three independent experiments are presented. (B) Treatment with CQ or BafA1 suppressed the formation of AVOs. HepG2 and Huh7 cells were treated with CQ (10 μM), BafA1 (20 nM), with or without MLN4924 (0.33 μM) for 72 hours. Formation of AVOs was examined under fluorescence microscopy. (C) Treatment with CQ or BafA1 enhanced MLN4924-induced cell proliferation inhibition. Cell viability was measured using the ATPLite assay (**P < 0.01, n = 3). (D) The combination of CQ or BafA1 with MLN4924 suppressed colony formation in liver cancer cells. Representative images are shown in the upper panels and statistical results are shown in the lower panels (**P < 0.01; n = 3).
