Figure 1.
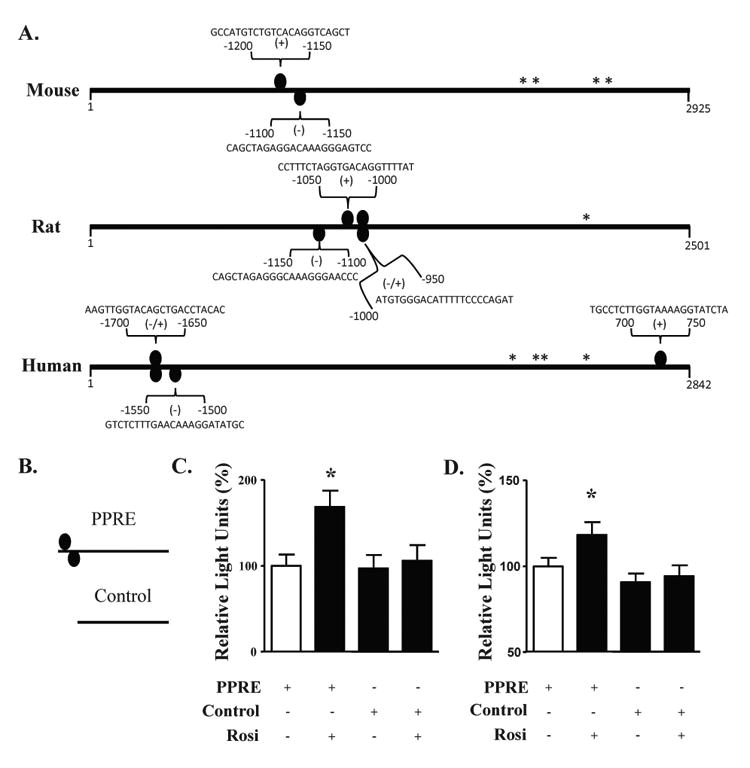
The mouse NF-α1 promoter contains PPARγ binding sites that are functional in neurons. (A) PPARγ binding sites (PPRE, ovals) are found in mouse, rat and human NF-α1 promoters. * indicate transcription start sites and the numbers represent the base pair position relative to the first transcription start site. Sequences are the PPARγ binding sites as determined by the Genomatix software. (B) Schematic diagram of the luciferase constructs containing a fragment of NF-α1 promoter without (control) or with the mouse PPREs. (C, D) Bar graphs showing luciferase activity from cortical (C) and hippocampal neurons (D) treated with and without rosiglitazone and transfected with a PPRE-containing construct, compared to neurons transfected with the control construct containing no PPRE. In both cell types, an increase in promoter activity was found when the cells were treated with Rosi. n=13/group for cortical neurons and n=36/group for hippocampal neurons; values are mean ±SEM, *p<0.05, one way ANOVA.
