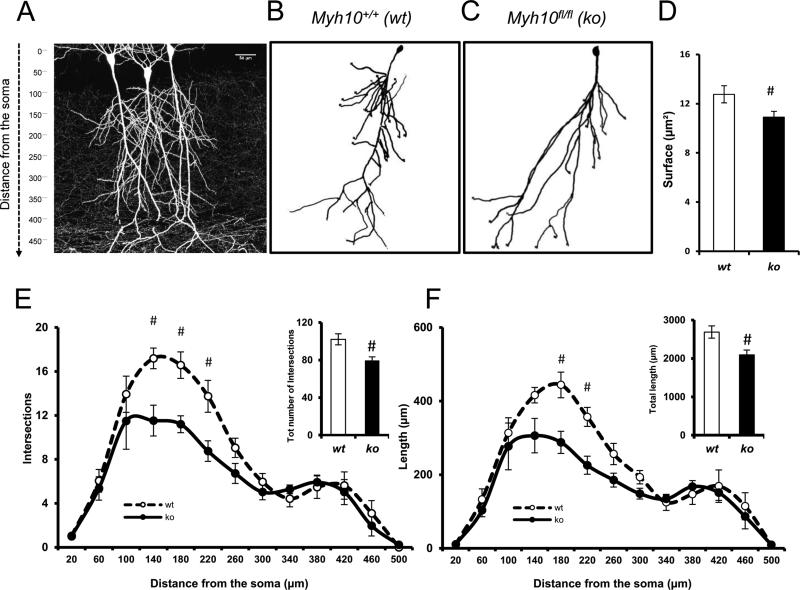
Figure 3. NM IIB ablation selectively disrupts the development of proximal dendritic branches in CA1 neurons.
(A) Photomicrograph multiphoton image of a portion of hippocampal CA1 showing labeled pyramidal neurons. (B-C) Representative 3D pyramidal hippocampal cell reconstruction using Neurolucida software. Neuronal complexity was measured applying the Sholl ring analysis method; (D) Bar graphs showing surface extension of traced apical arbors in both wt (14 neurons, n= 7 slices, n=5 mice) and ko (12 neurons, n= 6 slices, n=4 mice); p < 0.05. (E-F) Graphs exhibiting arbor complexity of pyramidal neurons in both wt and ko, measured as a number of intersections [RMANOVA, F1,12 = 2.4170; p < 0.01]) or cumulative length [RMANOVA, F(1,12) = 2.0649; p < 0.05] in relation to the distance from soma (insets depicting the total number of intersections and the total length, respectively); A LSD post-hoc test was applied where appropriate; # p<0.05 wt vs. ko comparisons. Error bars represent SEM.