Fig 5. The rhHSP70-induced ATP release contributes to endothelial Ca2+ oscillations.
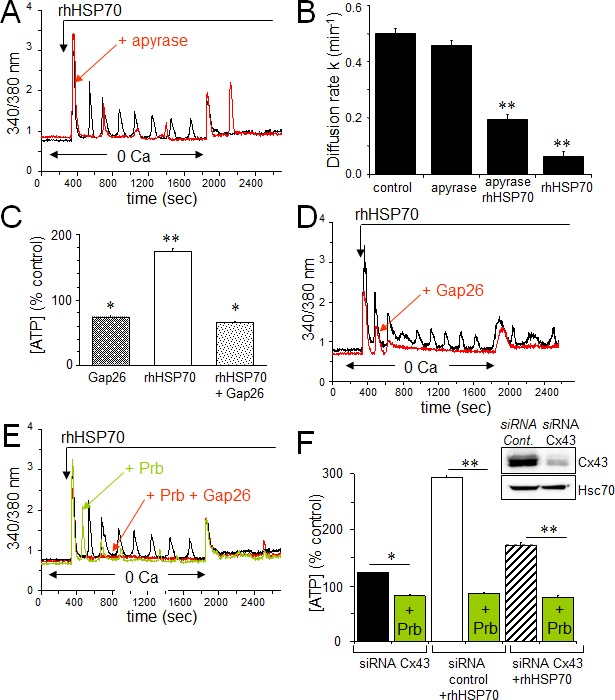
A. Contribution of the ATP release to the rhHSP70-evoked Ca2+ oscillations in HMEC. Cells were either untreated (black) or pretreated for 30 min with 20 U/ml apyrase (red) before to be exposed for 60 min to rhHSP70 (representative of 20 cells; n=5). B. Apyrase partially antagonizes the inhibitory effect of rhHSP70 on the GJIC between HMEC pretreated by apyrase then apyrase plus rhHSP27. Histogram shows the diffusion k constant measured after 60 min of cell treatments (mean ± SD, n=4; P-values<0.05 vs control). C. rhHSP70-induced ATP release from HMEC is blocked by Gap26 (500 μM). Extracellular ATP was measured by Luciferase assay (means ± S.D., n=3, P-values<0.05 vs control). D. Contribution of Gap26-sensitive channels to the rhHSP70-induced Ca2+ oscillations. Cells pretreated with Gap26 (500 μM for 30 min; red) before rhHSP70 (representative of 20 cells; n=5). E. Pannexin-1 modulates the Ca2+ oscillatory response to rhHSP70. Superimposed traces obtained from cells stimulated with rhHSP70 in the presence or absence of the Panx-1 blocker, 100 μM probecenid (Prb; green), or Prb plus Gap26 (red) (Representative of 10 cells; n=5). F. siRNA Cx43 knockdown attenuates the rhHSP70-induced ATP release. HMEC were transfected with Cx43 and control siRNA 48 h prior to various analyses. Insert is representative western blot showing the specific depletion of Cx43. Histogram shows the amounts of ATP released (relative to control cells) in response to rhHSP70 (1h). In some cases, transfected cells were exposed to 100 μM Prb (mean values ± SD, n=5; **P<0.01, *P<0.05 vs control).
