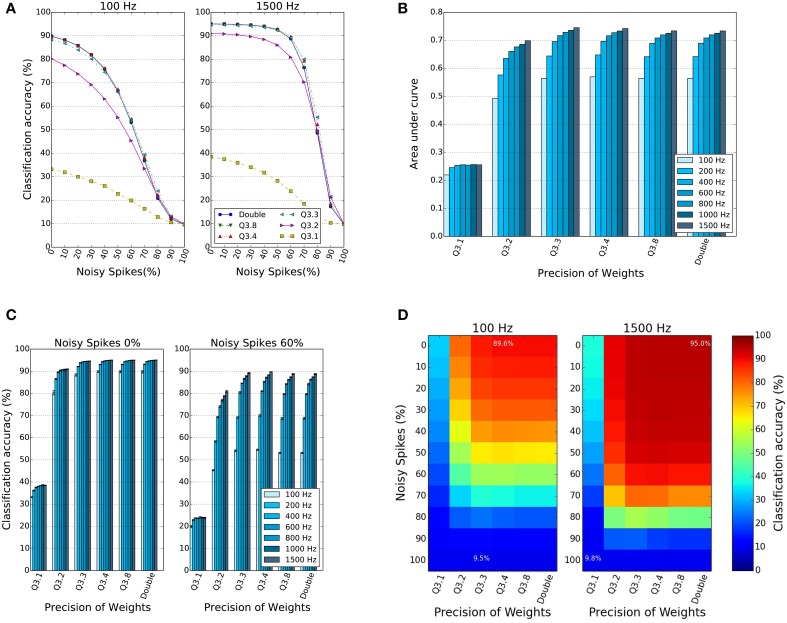
Figure 4.
Effect of reduced weight bit precision and input noise on the classification accuracy (CA). (A) CA as a function of input noise and bit precision of synaptic weights for two specific input spike rates of 100 and 1500 Hz. Results over four trials. (B) Normalized area under curve in (A) for different percentages of input noise, input firing rates and weight bit precision. Higher values mean higher accuracy and better robustness to noise. (C) CA as a function of the weight bit resolution for different input firing rates and for two different noise levels, 0 and 60%. (D) CA as a 2D function of the bit resolution of the weights and the percentage of input noise for 100 and 1500 Hz input rate. The results confirm that spiking DBNs with low precision weights down to f = 3 bits can still reach high performance levels and tolerate high levels of input noise.