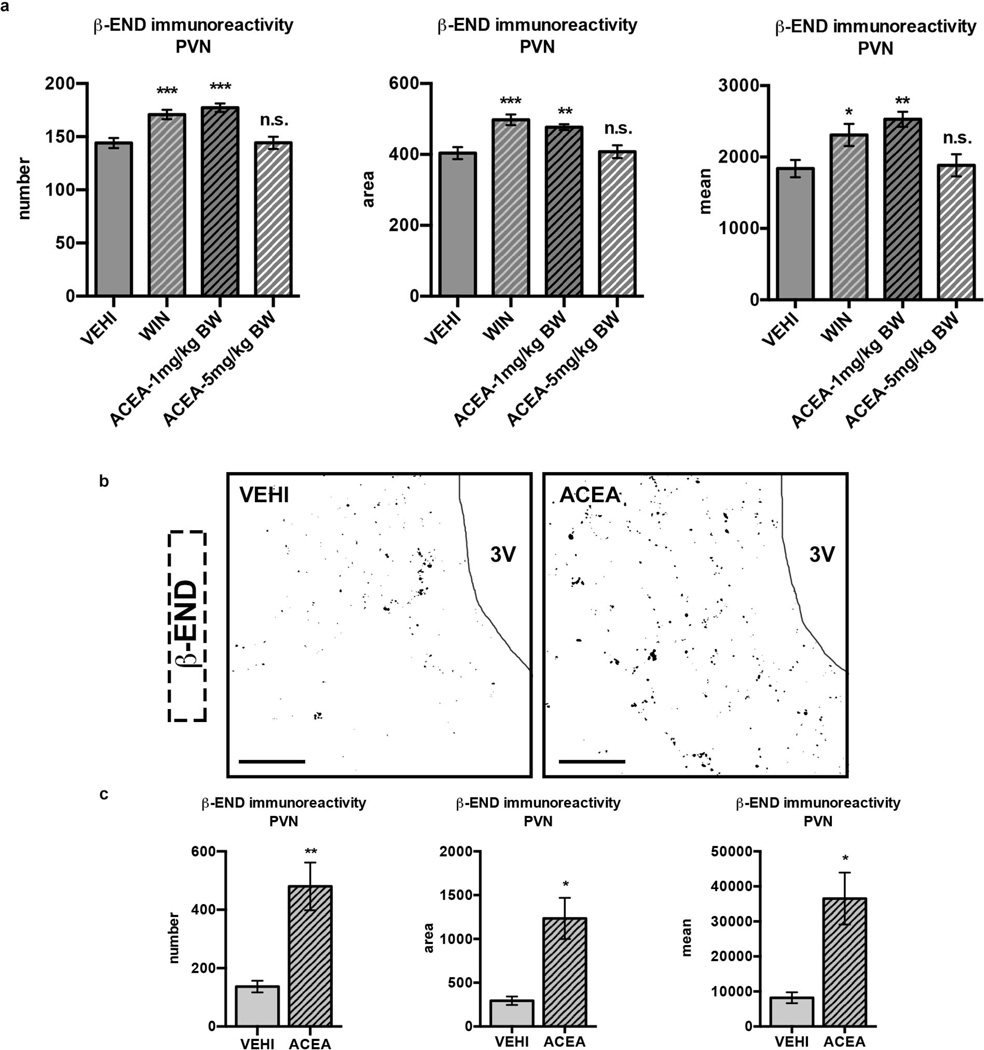
Extended Data Fig. 4. Bimodal character of ARC CB1R-driven β-endorphin increase.
a Compared to VEHI (bilateral PVN analysis; n=22 values/11 sections/4 mice), hyperphagic doses (1 mg/kg BW, respectively) of WIN (n=24/12/4) or ACEA (n=18/9/3) induced PVN β-endorphin immunoreactivity. Neutral dose (5 mg/kg BW) of ACEA (n=18/9/3) on feeding showed no effects (all values, see Supplementary Data Table 2). b Representative binary images of β-endorphin immunoreactivity after thresholding (image segmentation) using imagej software (for more details, see methods). c Compared to VEHI (unilateral PVN analysis; n=4 mice, 2–3 section/mouse), central, hyperphagic local ARC injection of ACEA (n=5 mice, 3 sections/mouse) increased PVN β-endorphin immunoreactivity (all values, see Supplementary Data Table 3). All quantified results ± s.e.m. If not otherwise stated, P values (unpaired comparisons) by two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars; 100 µm.