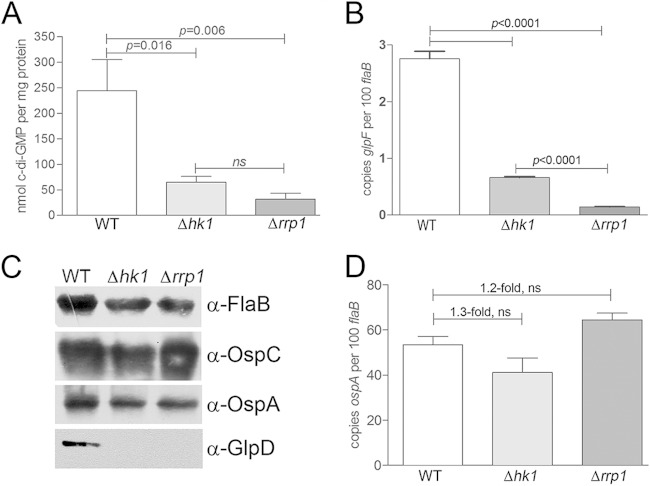
FIG 3.
Hk1 and Rrp1 function cooperatively to promote the synthesis of c-di-GMP and expression of c-di-GMP-dependent genes. (A) Intracellular levels of c-di-GMP in whole-cell lysates from B. burgdorferi wild-type (Bb1399), Δhk1 (Bb1197), and Δrrp1 (Bb1451) strains grown in vitro following a temperature shift from 23°C to 37°C (three biological replicates per strain), as measured by UPLC/MS/MS (135). The statistical significance of the difference in the results between the wild-type parent and each mutant was determined using an unpaired t test. ns, not significant. (B) Transcript levels for bb0240 (glpF) in B. burgdorferi wild-type, Δhk1, and Δrrp1 strains assayed by qRT-PCR. Values represent the average transcript copy numbers for bb0240 (glpF) ± SEM normalized per 100 copies of flaB from at least three biological replicates. Statistical significance was determined by comparing the average normalized copy number values for either mutant with those for the wild-type parent. (C) Whole-cell lysates from B. burgdorferi wild-type, Δhk1, and Δrrp1 strains grown to late logarithmic phase in vitro following a temperature shift from 23°C to 37°C were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using antisera against FlaB (loading control), OspC, OspA, and GlpD. (D) Transcript levels for ospA in B. burgdorferi wild-type, Δhk1, and Δrrp1 strains grown to late logarithmic phase in vitro following a temperature shift. Values represent the average transcript copy numbers for ospA ± SEM normalized per 100 copies of flaB from at least three biological replicates.