Figure 3.
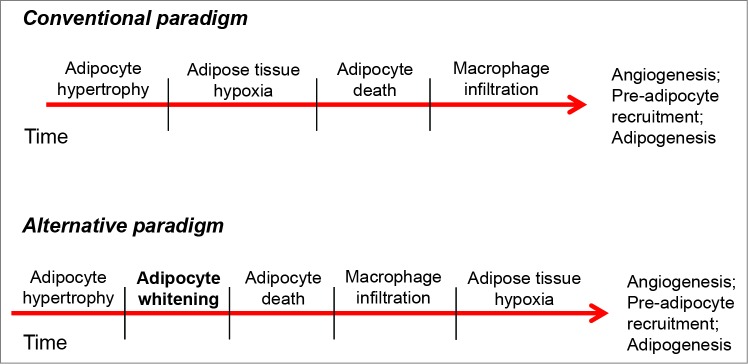
Potential role of adipocyte whitening in the adipose tissue remodeling paradigm. In the conventional view, chronic nutrient excess promotes excessive adipocyte hypertrophy, which contributes to adipose tissue hypoxia, necrotic cell death, and macrophage infiltration. Inclusion of the adipocyte whitening program could change this paradigm. Here, adipocyte hypertrophy is followed in time by decreases in mitochondrial abundance (whitening), which diminishes the capacity of the adipocyte to provide energy for itself. This results in adipocyte necrotic cell death, which is followed by a large influx of inflammatory cells having high metabolic activity. The relatively high rate of oxygen consumption by macrophages leads to adipose tissue hypoxia, which, in turn, is important for signaling for angiogenesis and the recruitment of new pre-adipocytes to aid in tissue remodeling.
