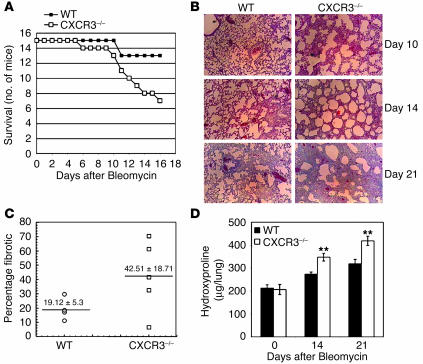
Figure 1.
Increased mortality from progressive lung fibrosis in CXCR3–/– mice following bleomycin-induced lung injury. (A) CXCR3–/– mice and WT C57BL/6J control mice were treated intratracheally with bleomycin. By day 14, 53.4% of CXCR3–/– mice were dead, whereas only 13.4% mortality was seen in WT mice. (B) Lung sections of CXCR3–/– or WT mice 10, 14, and 21 days after bleomycin instillation were stained with trichrome and counterstained with hematoxylin. Magnification,×100. Seven mice in each group were examined, and similar results were observed. Note that WT mice showed typical bleomycin-induced lung injury, whereas CXCR3–/– mice exhibited dramatic collagen staining. (C) Lung fibrosis after trichrome staining was quantitated by a pathologist in a blinded manner. The fibrotic area is presented as a percentage. *P = 0.05. (D) Lung tissue from CXCR3–/– mice and WT controls 14 and 21 days after bleomycin treatment was collected and assayed for collagen content using a conventional hydroxyproline assay. This is representative of three similar experiments. **P < 0.05.