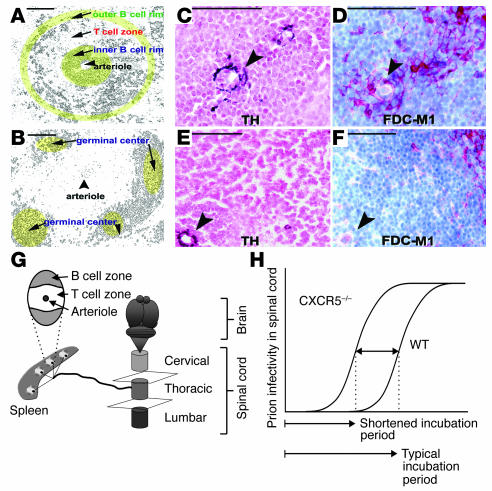
Figure 2.
Positioning of FDCs in spleens of WT and CXCR5–/– mice. (A and B) Diagrammatic representation of white pulp follicles in prion-infected CXCR5–/– and WT mice. Anti-CD21 immunostaining was performed to visualize the lymphoid white pulp follicle microarchitecture. (C) Atypically localized perivascular FDCs in lymph follicles in CXCR5–/– mice. Sympathetic nerves, visualized with antibodies to tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), are in close vicinity to FDCs (visualized by FDC-M1 immunostaining) (D). Scale bar: 50 mm. In contrast, sympathetic nerves in WT FDCs are localized in B cell areas at the periphery of the follicles (E and F). Arrowheads indicate TH and FDC-M1 positive areas. (G) Sympathetic nerves lining the thoracic spinal cord connect lymphoid organs and the CNS. (H) Shortened prion disease incubation period in CXCR5–/– mice inoculated intraperitoneally, relative to WT controls.