Figure 2.
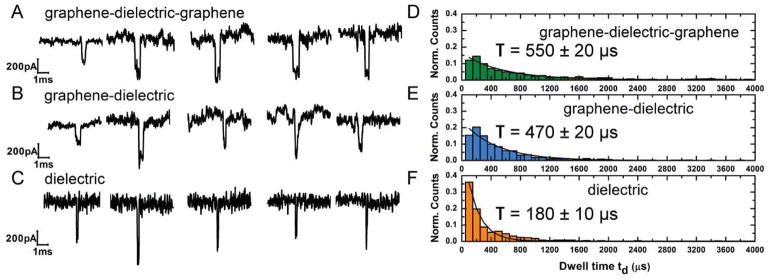
Experiments indicating the effect of graphene layers in slowing ssDNA translocation. A–C) Sample current blockades for 100 nt ssDNA for each membrane system of graphene–dielectric–graphene, graphene–dielectric, and dielectric respectively. All experiments were performed in 1 M KCl, 10 × 10−3 M Tris, 1 × 10−3 M EDTA at pH 7.6 and a transmembrane voltage of 300 mV. The sample traces show considerable slowing down with the introduction of graphene layers at the membrane area. D–F) Translocation time histograms for the cases A–C, respectively. With 100nt ssDNA we find average translocation times of T = 550 ± 20 μs, T = 470 ± 20 μs, T = 180 ± 10 μs for graphene–dielectric-graphene, graphene–dielectric, and dielectric, respectively. Graphene DNA hydrophobic interactions reduce the translocation velocity of the DNA molecule by about 3 times when compared to translocation properties of the purely dielectric membrane.
