Figure 1.
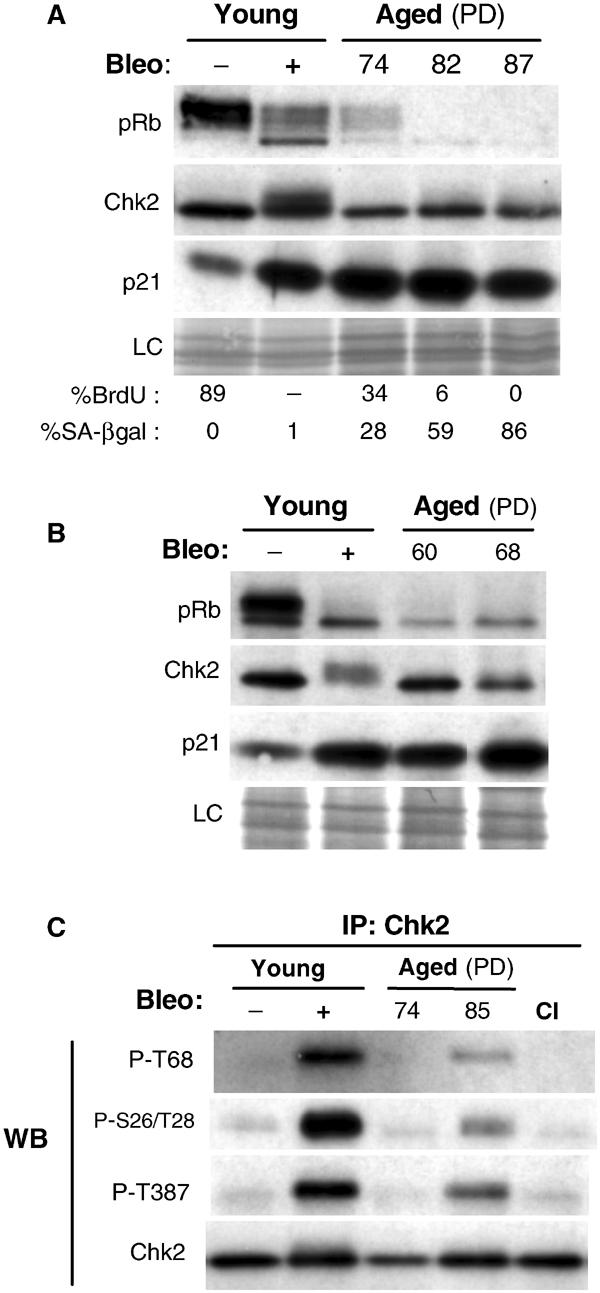
Chk2 activation at replicative senescence. (A) Abundance and status of pRb, Chk2 and p21 of fibroblasts at different PDs up to senescence. Western blot analysis of young fibroblasts at PD35 untreated (−) or treated (+) with bleomycin (bleo) (used here as positive control) and ageing fibroblasts at PD74, PD82 and PD87 (cell population fully senescent). Loading control (LC) is the scan of amido-black-stained membrane, which showed equal amounts of protein transferred. The phosphorylation status of Rb is used to monitor cell cycle regulation. The percentages of cells positive for BrdU (24 h labelling) and SA-βgal are shown below. The standard deviations were 1–3%. Positive cells were scored by microscopic observation after indirect immunostaining of BrdU incorporation and histochemical assessment of β-galactosidase activity at pH 6. (B) Similar analysis for young and aged IMR90 fibroblasts at PD60 and PD68 (cell population fully senescent). (C) Chk2 phosphorylation at senescence. Phosphorylation at Thr68, Ser26/Thr28 and Thr387 was examined with phospho-specific antibodies on immunoblots of Chk2 immunoprecipitates from lysates of young fibroblasts untreated (−) or treated (+) with bleomycin (bleo), and of aged and young contact-inhibited (CI) fibroblasts. Recovery of immunoprecipitated Chk2 was monitored by immunoblotting with total Chk2. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot.
