Figure 1.
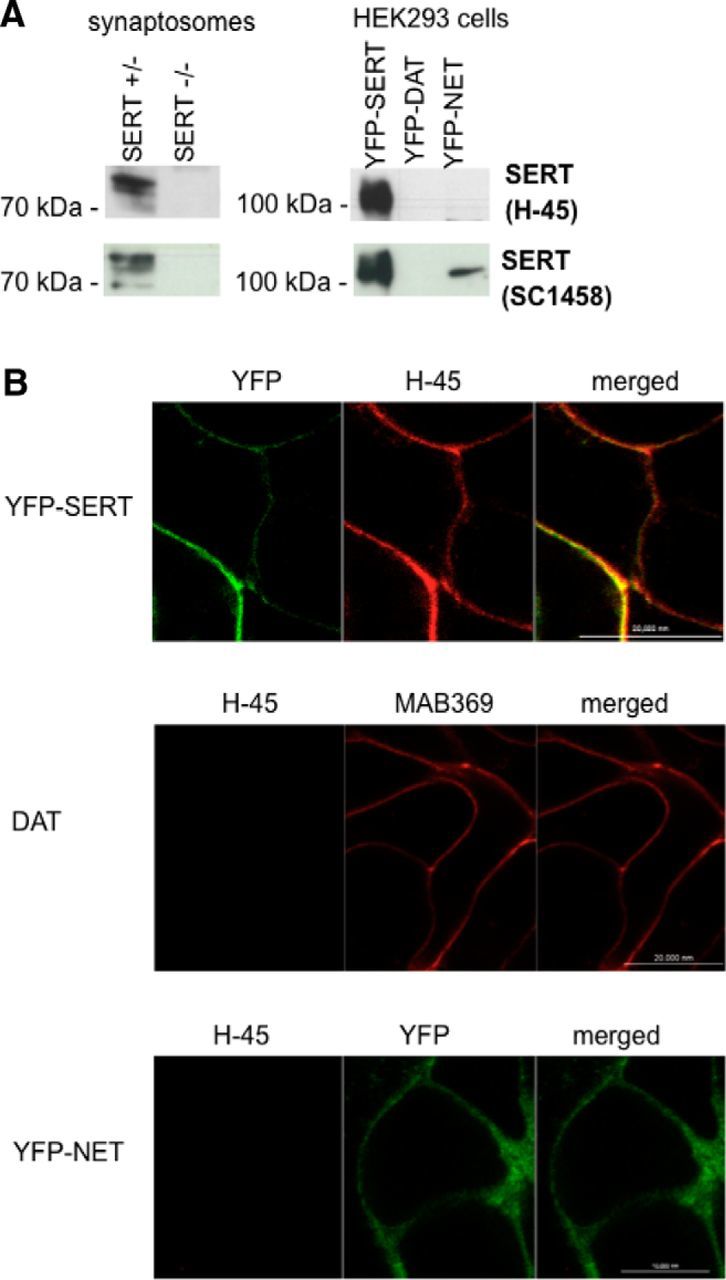
Specificity of the mouse monoclonal (H-45) SERT antibody. A, Hippocampal synaptosomal proteins (15 μg/lane) were prepared from wild-type and SERT-deficient mice (left blots); cell membranes (15 μg/lane) were prepared from HEK293 cells stably expressing YFP-tagged human SERT (YhS), DAT (YhD), and NET (YhN) (right blots). After electrophoretic resolution and transfer of the proteins, immunoreactive bands were detected with the H-45 monoclonal anti-SERT antibody (top row) or with a commercially available SERT antibody (sc-1458) (bottom row). B, YFP-tagged SERT expressed in HEK293 cells was visualized by confocal microscopy by either its fluorescent tag or immunostaining of fixed cells with the anti-SERT H-45 antibody using an Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated secondary antibody (top). The cells were washed, and the fluorescence was visualized by confocal microscopy. Merged images are shown on the right side to illustrate the colocalization. HEK293 cells expressing human DAT (DAT, top) or YFP-tagged human NET (YFP-NET, bottom) were fixed and stained with the DAT-directed antibody MAB369 (top) and the anti-SERT antibody H-45. Immunofluorescence and YFP fluorescence were imaged by confocal microscopy. Representative data are shown that were reproduced in at least one independent experiment.
